* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download roots, stems, and leaves
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
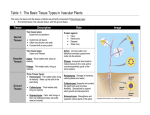
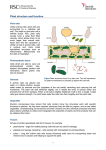
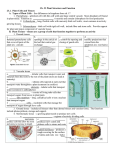
Roots, Stems, and Leaves • The three main plant organs are roots, stems, and leaves. • These organs are made up of three main kinds of tissues: – dermal tissue – vascular tissue – ground tissue. Plant Tissues • Dermal tissue – – the “skin” of a plant. – protects the plant and prevents water loss. Plant Tissues cont. • Vascular tissue – moves water and nutrients throughout the plant. • Xylem tissue – moves water. – made up of tracheids and vessel elements. • Phloem tissue – moves sugars. – consists of sieve tube elements and companion cells. Plant Tissues cont. • Ground tissue– all the cells that lie between dermal and vascular tissues. – made up mostly of parenchyma cells. • Parenchyma cells have thin cell walls and function in photosynthesis and storage. – Collenchyma and sclerenchyma • These cells have thick cell walls that help support the plant. Plant Tissues cont. • Meristematic tissue– responsible for plant growth. – Produces new cells by mitosis. – Develop specialized structures and functions when mature in a process called differentiation – found at the tips of stems and roots. Roots • 2 types of roots– Taproot : One big primary root + small secondary roots – Fibrous root: Primary and secondary roots = same size • Functions: – anchor a plant in the ground. – absorb water and dissolve nutrients from the soil. • Root pressure forces water upward through the xylem toward the stem. Stems • Functions: – They produce leaves, branches, and flowers. – They hold leaves up to the sunlight. – They also carry water and nutrients between roots and leaves. • Arrangement of tissues – Monocots: vascular bundles are scattered – Dicots : vascular bundles are arranged in a ring. • These vascular bundles contain xylem and phloem tissue. • Growth: – Primary : grows longer – Secondary: grows wider Leaves • main organs of photosynthesis. – make food (sugars) – made up of a specialized ground tissue called mesophyll cells. • Mesophyll : many chloroplasts responsible for photosynthesis • veins : Xylem and phloem tissues • Stomata: small openings – prevent water loss. Transport in Plants • Capillary action: – Cohesion- forces between water and water molecules – Adhesion – forces between water and other molecules • Transpiration pull – water moves from areas where there is plenty of water to areas where there is little water. • Pressure-flow hypothesis – explains how phloem transport happens • sugars move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. Which part is responsible for photosynthesis? D C B A If a plant becomes too dry, are the stomata in the leaves more likely to be open or closed? • Which tissue is found in the center of a plant stem? – A. dermal tissue – B. vascular tissue – C. ground tissue • Which of the three kinds of ground tissue serve mainly for storage? – A.parenchyma – B. collenchyma – C. sclerenchyma • Cells that can differentiate into many plant tissues are found in A. the vascular cylinder. B. dermal tissue. C.meristematic tissue. • Photosynthetic tissues in a leaf include the – A.phloem. – B.vein. – C.palisade mesophyll. • A process in which water is lost through the leaves of a plant is called – A.transpiration. – B.photosynthesis. – C.glycolysis.