* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Systems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
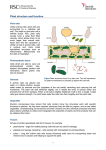
Plant Systems Part II Plant Tissues • A tissue is a group of cells working together to perform a similar function. – The cells in tissues are specialized to perform specific functions. – All these cells develop from unspecialized cells during cellular differentiation Recall: what were unspecialized cells called in animals? Stem Cells! • In plants, these cells are not called stem cells – they are called meristematic cells • A region of a plant that is rich in meristematic cells is called the meristem region Tissue Systems • Plants have 3 major tissue systems: 1. Dermal • Covers outer surface of plant 2. Vascular • • Found in every root, shoot and leaf System is continuous (all plant parts joined by vascular tissues) 3. Ground • All other tissues Dermal Tissue System Epidermal Tissue Thin layer of cells covering all non-woody surfaces of a plant Periderm Tissue Tissues on the surface of the plant that produce bark on stems and roots Dermal Tissue System Dermal Tissue System Cells of the Dermal tissue system: – Epidermal root cells have extensions (root hairs) to absorb water and minerals – Epidermal leaf cells produce a layer of wax to waterproof surface – Some have developed for defense purposes Vascular Tissue System • This is the transportation system that moves water, minerals and other chemicals around the plant • All vascular tissues are connected Vascular Tissue System Xylem Transports water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves and stems Phloem Transports dissolved food materials and hormones throughout the plant Vascular Tissue System Vascular Tissue System Xylem – Transports water and dissolved minerals upwards from the roots – Cells are hollow tubes with rigid walls • No cytoplasm, nucleus or organelles (allows for easier transportation of water) – MATURE xylem cells are not considered living tissue Vascular Tissue System Phloem – Transports sugars produced by photosynthesis (and hormones) – Phloem can move sugars downwards from the leaves and stems or upwards from the roots – Phloem cells are alive when functioning Ground Tissue System • The ‘filler’ between dermal and vascular tissues • Functions: – In green parts of plant, they manufacture nutrients via photosynthesis – In stems, they provide storage and support – In roots, they store carbohydrates Photosynthesis – Tissues Working Together • Because sugar (glucose) is so important to all components of a plant, it must have a system in place to transport the sugars • Oxygen is also required by plant cells (for cellular respiration) – Leaves produce more O2 than is needed, and any excess is released as waste Recall: Plants and Food - Since plants cannot move like animals do to obtain food, they must make their own food through a process called photosynthesis. light energy + carbon dioxide + water glucose + oxygen glucose Photosynthesis – Absorbing Light light energy + carbon dioxide + water glucose + oxygen • Leaves that are wide and thin are ideal for light absorption. Why? – Greater SA Remember: Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts Photosynthesis – Absorbing Light • Chloroplasts are contained in the mesophyll layers – Palisade mesophyll is located where there is maximum light – Spongy mesophyll is located throughout leaf with air pockets in between • Mesophyll layers as a whole are part of ground tissue system Photosynthesis – Obtaining CO2 • CO2 will naturally diffuse into a leaf. To avoid too much diffusion, the leaf is coated with a layer of epidermal tissue called the cuticle • Gases enter and exit through openings in the leaf called stomata • Stomata are controlled by guard cells. Photosynthesis – Obtaining Water • Leaves will close their stomata when water levels are low • Leaves obtain water through vascular tissues (xylem and phloem) – Arranged as bundles called vascular bundles and run from root to leaf – Root hairs (epidermal) grow into soil from roots and obtain water via diffusion – Water is transferred via xylem, from the roots to the leaves 1. What is a tissue? 2. Name the three tissue types in plants and briefly describe their function. 3. What is the difference between dermal and periderm tissues? 4. Describe the difference between the xylem and phloem. 5. What is the difference between the spongy and palisade mesophyll? 6. How does the shape of a leaf help photosynthesis take place? 7. What is a stomata? How do the guard cells open and close?