* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plants-Flowers
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
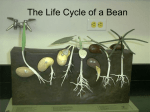
Plants “Flowers” 6th Grade Science 4th Quarter 6.L.1 The Plant Kingdom • This kingdom has organisms that are multi-cellular, have cell walls and chlorophyll, produce their own food, and don’t physically move from one place to another. Plants: Grouped by characteristics • Vascular – Three main parts: roots, stems and leaves • Roots can be different sizes: – Fibrous and tap roots • Storage roots; beets, carrots, sweet potatoes and turnips – Roots have different functions: anchoring the plant, tak water and minerals, and store food. • Nonvascular – Simple; most grow in moist places – No vascular tissues. What do plants do? • All plants are alike in one way. – They need three things in order to survive • Water • carbon dioxide • energy from sunlight – What do you suppose the plants Classify – use these things for? to sort into groups based on similarities and differences The Plant Kingdom • • • • • • Photosynthesis Plant Cell Parts of a Flower SOL Released Test Items Vascular Non-Vascular Photosynthesis • Plant cells produce their own food through a process called photosynthesis. • Photosynthesis allows plants to convert light energy into food energy. Photosynthesis • process by which CO2 and H2O in the presence of light are converted to sugar and oxygen • https://www.brainpop.com/science/cellularlifeandgenetics/photosynthesis/ • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lDwUVpOEoE4 Chemical formula • 6CO2 + 6H2O • -----> in reaction with sunlight and chlorophyll ------> • C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2 • http://studyjams.scholastic.com/studyjams/jams/scienc e/plants/photosynthesis.htm food • manufactured in the leaves moves downward through the stem to the roots –used by the plant –stored in stem or root and leaf in the form of sugar, starch or protein. They turn it into sugar! photosynthesis – a process by which plants change light energy from the sun and use it to make sugar Plants and some protists conduct photosynthesis. Photosynthesis A movie of photosynthesis As a plant makes sugar, oxygen is released When the plant uses the sugar, water and carbon dioxide are released. chlorophyll – the green substance found in plants that traps energy from the sun and gives plants their green color carbon dioxide – a gas found in air Plant Cell chloroplasts cell wall nucleus cell membrane cytoplasm vacuoles – Because of this process • Scientists are able to classify living things by the way they get their food. – Plants are producers (autotrophs) producer – it is a living thing that uses sunlight to make sugar. This sugar feeds others. Respiration • plants respire 24 hours a day • Plants usually give off more O2. • consume some O2 and give off some CO2 • plants produce more O2 through ps. Than they consume during respiration and growth. Resipiration • Humans will use most of the oxygen given off by plants and they will release CO2. • Plants in return use the CO2 during photosynthesis • http://studyjams.scholastic.com/studyjams/jams/scienc e/ecosystems/carbon-cycle.htm Plants reproduce differently Reproduce – it means “to make more of the same kind” Plants are classified by characteristics. Plants that make seeds Flowering Plants Conifers Plants that do not make seeds Ferns Mosses a protective covering that surrounds the seed makes seeds. makes the plant's food. anchor the plant in place and absorb water and other minerals from the soil. carries water and food to the rest of the plant. How Do Flowers Make Seeds and Fruits? Great Plant EscapePlant parts Ovary – the bottom part of the pistil in which seeds form Ovule - the inner part of an ovary that contains an egg embryo – tiny part of a seed that can grow into a new plant How Seeds Form • After fertilization the flower dries up and petals fall off, leaving just the pistil and its ovary. • The top of the pistil falls off and the ovary gets larger as one or more seeds form inside it. • When the seeds are formed, the ovary dries up and the seeds fall out. • Corn, Beans, and Peas are seeds that we eat • http://studyjams.scholastic.com/studyjams/jams/science/plants/plant -with-seeds.htm How Fertilization Occurs • When a pollen grain reaches a pistil, it grows a thin tube to the ovary. Sperm from the pollen grain combines with an egg, and a seed forms. Fertilization – the combination of sperm from a pollen grain with an egg to form a seed How Pollination Occurs • Butterflies may carry pollen from the stamen of one flower to the pistil of the the same flower. Sometimes the butterfly may carry pollen from the stamen of one flower to the pistil of another flower of the same kind. • Pollen: Nothing to Sneeze At Pollination- the movement of pollen • https://www.brainpop.com/scie from a stamen to a nce/cellularlifeandgenetics/poll pistil ination/ Some flowering plants are monoco t seed – a seed that has one seed leaf and stored food outside the seed leaf dicot seed – a seed that has two seed leaves that contain stored food What is the Life Cycle of a Flowering Plant • Dormant Seed – Takes in water and the seed coat gets soft. If the seed has enough oxygen and the right temperature, it will begin to germinate. – https://www.brainpop.co dormant – the m/science/cellularlifeandg resting stage of a enetics/plantgrowth/ seed Seed Reproduction 3 Germination • A series of events that results in the growth of a plant from a seed is called germination. • Seeds will not germinate until environmental conditions are right. • https://www.brainpop.com/ science/cellularlifeandgen etics/pollination/ Seed Reproduction 3 Germination • Temperature, the presence or absence of light, availability of water, and amount of oxygen present can affect germination. Seed Reproduction 3 Germination • Germination begins when seed tissues absorb water. • This causes the seed to swell and the seed coat to break open. • Next, a series of chemical reactions occurs that releases energy from the stored food in the cotyledons or endosperm for growth. Seed Reproduction 3 Germination • Eventually, a root grows from the seed, followed by a stem and leaves. • Geminating Seed – First a root pushes through the seed coat and grows downward. – The top part of the root grows upward and becomes the stem. The stem carries the seed coat and the seed leaves with it. The seed coat falls off. The seed leaves provide food for the plant. Two small leaves begin to grow from between the seed leaves. • Seedling When the stored food within the original seed leaves is used up, they dry up and drop off. More leaves grow from buds on the stem as the plant grows taller. The new leaves can trap energy from sunlight and make sugar. Plants use the energy in the sugar to grow. https://www.brainpop.com/science/diversityoflife/seed nts/ Seed Reproduction 3 Seeds • A seed consists of an embryo, stored food, and a protective seed coat. • The embryo has structures that eventually will produce the plant’s stem, leaves, and roots. Seed Reproduction 3 The Flower • Most flowers have four main parts—petals, sepals, stamen, and pistil. Seed Reproduction 3 Seed Development • Seeds of land plants are capable of surviving unfavorable environmental conditions. 1. Immature plant 2. 3. Cotyledon(s) Seed coat 4. Endosperm Seed Reproduction 3 Seed Dispersal • Plants have many ways of dispersing their seeds. • Most seeds grow only when they are placed on or in soil. • They fall onto the soil from the parent plant on which they grew. Seed Reproduction 3 Seed Dispersal • In nature some seeds can be spread great distances from the parent plant. • Wind dispersal • usually occurs because a seed has an attached structure that moves it with air currents. Seed Reproduction 3 Seed Dispersal • Animals can disperse many seeds. • Some seeds are eaten with fruits, pass through an animal’s digestive system, and are dispersed as the animal moves from place to place. • Attaching to fur, feathers, and clothing is another way that seeds are dispersed by animals. Seed Reproduction 3 Seed Dispersal • Water also disperses seeds. • Raindrops can knock seeds out of a dry fruit. • Some fruits and seeds float on flowing water or ocean currents. Seed Reproduction 3 Importance of Flowers • The appearance of a plant’s flowers can tell you something about the life of the plant. • Large flowers with brightly colored petals often attract insects and other animals. Seed Reproduction 3 Importance of Flowers • As they move about the flower, the animals get pollen on their wings, legs, or other body parts. • Later, these animals spread the flower’s pollen to other plants that they visit. Seed Reproduction 3 Importance of Flowers • Other flowers depend on wind, rain, or gravity to spread their pollen. • Their petals can be small or absent. Parts of a plant • Four basic parts –leaves –stems –roots –Flowers – http://studyjams.scholastic.com/studyjams/jams/sc ience/plants/flowers.htm What Are the Parts of a Flower • Most flowers have four parts Sepal – one of the leaf-like parts that protects a flower bud and that is usually green – Flower parts Pistil – part of a flower that makes the eggs that grow into seeds Stamen – part of a flower that makes pollen Pollen – tiny grains that make seeds when combined with a flower’s egg Parts of a Flower Male Parts Female Parts Parts of a Flower Male Parts Female Parts The stamen consists of two parts: the anther and the filament. The filament holds the anther. The anther produces and carries the pollen. Parts of a Flower Male Parts Female Parts The pistil consists of three parts: the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is the sticky part that traps and holds the pollen. The style is the tube-like structure that holds up the stigma. The ovary and the ovule are at the bottom of the style. Parts of a Flower Male Parts Female Parts The petals attract pollinators. (bees, hummingbirds, butterflies, for example) Parts of a Flower Male Parts Female Parts The sepals are the green petal-like parts at the base of the flower. Sepals help protect the developing bud. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-qKWw7JcXCY Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds • pollination- color of flower attracts insects to fertilize flower – beginning of fruit and seed formation • fruits and seed are attractive to birds who eat and spread seeds. – Reproduces plant – some seeds carried on animals coats Parts of the Flower • differ in size, shape, and color, some basic parts • sepal –green leaf-like part, covers and protects bud before opening Petals • are actually leaves • usually bright colors to attract pollinating insects. Parts of the Flower • stamens –male part of flower –has two parts •filament-stalk Anther • anther- sac-like structure on top of filament, contains pollen Parts of the Flower • Pistil - female part • in the center of flower • has three parts Pistil • three parts • stigma - top - sticky • style - tube leading from stigma to ovary Ovary • egg cells develop here • grows to become fruit or seedcoat