* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant_powerpoint - District 128 Moodle
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
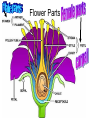
What is a plant? • Multicellular • Autotroph • Sounds like it could be a protist so far. • And the embryo develops within the mother plant. • Plants evolved from green algae Flower Parts • Pollen (male sperm) lands on the female stigma • Pollen travels down to the ovary and fertilizes the ovules (egg) • Develops into a seed What happens when a flower dies? • When a ovule becomes fertilized, the flower is no longer needed. • The petals fall off, and the seed needs some protection. • The ovary forms into a fleshy body to protect the seed. • A fruit is an ovary that has enlarged to protect a seed! Seeds can be protected in different ways. • When plants bear seeds that are ‘naked’, meaning not enclosed in an ovary they are called a______________. • When seeds are protected in a fruit, they are classified as a/n _____________. Do grasses have fruits? • Grasses have fruits! • Corn • Rice • Wheat Seed Anatomy See board for more info Seed Dispersal • Seeds have adapted so make it easier for them to land in different places and eventually grow into a new plant. • Stick to animals ( Burrs) • Edible fruits (fruits) • Travel by wind or water (helicopters/maple seeds, dandelions) Seed Germination • When a plant begins to grow, it needs favorable conditions. • They must soak up water!! • By taking up water, the seed expands and splits its seed coat. Asexual Reproduction • Remember cloning??? • Asexual reproduction in plants is called vegetative reproduction. • Many plants drop stems or shoots that develop into new plants (same DNA), and strawberries send out runners. Anybody like to have beautiful flowers but not want to have to plant them year after year? • Annuals – complete their life cycle (germinate, grow, produce flowers and seeds, and die) in one year. • Biennials complete the cycle in two years and flower the second year. • Perennials live and reproduce for many years. • Which type of flower would you plant and why? Plant structure • • • • Buds – undeveloped shoots (terminal =end of a stem) Blade – main part of the leaf Petiole – connects leaf to the stem • Leaf veins – carry nutrients to/from leaves Root types • Fibrous roots – a mat of thin roots spread out below the surface providing increased exposure to nutrients and water • Tap roots – characterized by one large vertical root with many smaller branches ex. carrots, turnips, and beets Stems – support and transportation • Vascular tissue – tubular cells used for transporting materials (like human veins) • Two Types – – Xylem – transports water and dissolved minerals upward from roots into the shoots – Phloem – transports food (glucose) made in the leaves down to the parts that don’t make their own food (roots) Plant Growth When a plant grows in length, this is called primary growth. Meristems – tissues that have cells going through mitosis Where is growth occurring? What protects the root? -Root cap If primary growth is growth in length, what is secondary growth? • Secondary growth is growth in width • Occurs in woody plants • Vascular cambium (actively going through mitosis) adds cells resulting in secondary growth • • secondary xylem – wood everything outside the vascular cambium is bark (made up of cork) What are tree rings? • Each year, the plant grows new vascular cambium cells. • In the summer, there is plenty of water to transport therefore the cells are _______. • Towards summer and fall, there is less water, and the cells are _______. • This creates a new tree ring each year. Oxygen out and carbon dioxide in Tropisms • Gravitropism – roots grow towards gravity • Phototropism – stems and leaves grow towards light (photo)