* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PLANT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
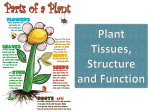
PLANT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION THE PHYLOGENY OF PLANTS… Charophytes (green algae) Bryophytes (non vascular) Trachoephytes (seedless, vascular) Gymnosperms (“naked seeds”,vascular) Angiosperms (contained seeds, vascular) Monocots / Dicots Major Parts of a Plant – Leaves Where photosynthesis occurs – Seeds Method of sexual reproduction – Flower Site where reproduction occurs – Stem Transports nutrients and supports the plant – Root take in nutrients and anchor plant The Seed Parts of a Seed – Cotyledon The first leaves of a plant – Seed Coat Outside covering of a seed – Endosperm Food storage tissue that nourishes the embryo – Embryo – New plant developed after fertilization Types of Seeds Monocots – A seed with only one cotyledon – All grasses are monocots – Flower parts in threes – Leaves with parallel primary veins Dicots – A seed with two cotyledons – Flower parts in fours or fives – Leaves with distinct vein network – All broadleaf plants are dicots Seed Parts Fertilizationzygoteseed (embryo) Plumule- is like a leave in its early development becomes the shoot Hypocotyl- develops into the stem Radicle- Becomes roots Male Parts of the Flower Stamen- Makes up all male parts Pollen- Male sex cell, similar to sperm Anther- Sac-like structure on top of the filament Filament- Short stalk that holds the anther Female Parts of the Flower Pistil- Makes up all female parts Ovules- Female sex cell, similar to the egg Stigma- Sticky part of the system, catches pollen Style-Tube that leads from the stigma to the ovary Ovary- Place where ovule is fertilized by the pollen, Turns into a fruit or seed coat Primary Growth Occurs in apical meristems of plant – (found at tips of stems and roots) PROBLEM! IF THE CUTICLE BLOCKS WATER, WHAT ELSE IS PREVENTED FROM ENTERING/EXITING THE PLANT? C O !! 2 Solution? STOMATA! – Tiny pores in epidermis surrounded by two guard cells! – Open during the day! Why? PS occurs during the day Transpiration necessary for cooling VASCULAR TISSUE 2 MAJOR TYPES: – XYLEM TISSUE – PHLOEM TISSUE – Found together in VASCULAR BUNDLES – Arise primarily from apical meristem – Arise secondarily from vascular cambium XYLEM TISSUE CONDUCTS WATER PROVIDES MECHANICAL SUPPORT 2 TYPES OF XYLEM CELLS: – TRACHEIDS: – VESSEL ELEMENTS: PHLOEM TISSUE CONDUCTS SUGARS COMPOSED OF TWO CELL TYPES: – SIEVE-TUBE MEMBERS – COMPANION CELLS Sieve tube members Form sieve tubes to conduct sugars throughout plant Lack nuclei, ribosomes, vacuoles, etc. Vascular bundle xylem Stems Transports food, water, and nutrients Supports the leaves and flowers Parts of the Stem – Xylem Water and minerals travel up to other plant parts – Phloem Manufactured food travels down to other plant parts – Cambium – Separates xylem and phloem Types of Root Systems – Fibrous Roots – Easier to transplant Short, small, compact roots – Tap Root – Difficult to transplant, since most of the tap root is cut-off Tap root is primarily used for storage of food In both types, most nutrients and water are absorbed by root hair Fibrous Roots – Monocots – Several roots of same size w/ branching Roots can be adapted for storage of nutrients: – Example: Carrot (Taproot) Sweet Potato (Fibrous Root) Plant Processes – Photosynthesis Mixes light, water, and carbon dioxide in the presence of chlorophyll to produce sugar and oxygen – Respiration Combines sugars and oxygen to give off water and heat – Transpiration – Loss of water through the leaves or stems – Causes wilting when soil is dry Animal Water Wind Dispersal of Seeds Gravity Wind Force Plant Systems There are 3 main plant systems: Reproductive – this is the flower structure Transport – this is the stem and roots and their xylem and phloem Energy – this is the leaf and other areas of photosynthesis. Leaf Tissue – What happens where?