* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Evolution - Cloudfront.net
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
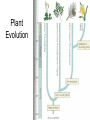
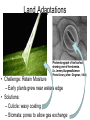
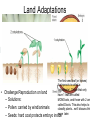
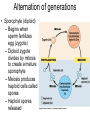
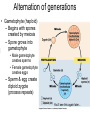
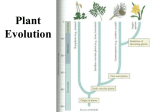
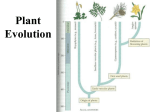
Plant Evolution Plant Evolution • Evolved from green algae (450 mya) – Evidence: Both have chlorophyll, store energy as starch, DNA similarities • Green algae ancestor – Multicellular body – Cells w/ channels to communicate – Reproduce w/ sperm & egg • Early plants – Low growth Okay, so we now know that plants evolved from green algae… What do we know about algae? Yeah- mostly aquatic & unicellular, some multicellular but low growth (nothing really above water) So, what sort of challenges do you think land plants had to over come? Land Adaptations • Challenge: Retain Moisture – Early plants grew near waters edge • Solutions: – Cuticle: waxy coating – Stomata: pores to allow gas exchange Land Adaptations • Challenge: Transporting Resources Vascular tissue consists of what’s called xylem (ZY-LUM)and phloem (FLO-M), that’s what the first picture on the left shows. The picture on the water) right is of a cross section from a plant stem. Those openings are (ex: sugars)where that vascular tissue is. – Solution: Vascular system- tissue to transport nutrients • Up from the roots (ex: • Down from the leaves – Allows taller growth Land Adaptations • Challenge: Growing upright – Large plants need to support own weight – Solution: Lignin- hardens cell wall; gives wood strength Land Adaptations • Challenge:Reproduction on land – Solutions: – Pollen: carried by wind/animals – Seeds: hard coat protects embryo The first seed leaf (or leaves) that sprouts is called a cotyledon(s). Those that only have 1 leaf are called MONOcots, and those with 2 are called Dicots. This also helps to classify plants…we’ll discuss this more later. inside Alternation of generations • Sporophyte (diploid) – Begins when sperm fertilizes egg (zygote) – Diploid zygote divides by mitosis to create a mature sporophyte – Meiosis produces haploid cells called spores – Haploid spores released Alternation of generations • Gametophyte (haploid) – Begins with spores created by meiosis – Spore grows into gametophyte • Male gametophyte creates sperms • Female gametophyte creates eggs – Sperm & egg create diploid zygote (process repeats) You’ll see this again later… Plant Ecology • Mutualistic relationships – Type of symbiosis where both organisms benefit – Ex: Plants (provides living space)/Bacteria (create nutrients) – Ex: Plants (provide food)/Insects (help pollinate) • Herbivore interactions – Defense adaptations – Spines, thorns, chemicals, What to do now?? You can start your homework if you’d like (dice pgs. 617-618 & 665) To do that (view the online textbook) you must have already created an account on classzone.com (you only need an account to view the online text…not to play games, etc.) If you want to create an account, please do! The access code is 2631090-10. Otherwise, you may work on anything else…as long as you’re PRODUCTIVE and not socializing!!! BE GOOD!