* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Evolution and Classification Power Point File
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
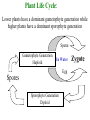
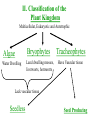
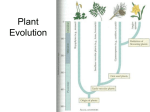
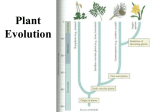
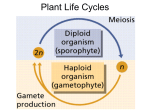
I. Plants and the Colonization of the Land A. An Introduction to the Plant Kingdom 1. Characteristics of Plants a) Autotrophic: Contain chlorophyll a & b, carotenes b) Multicellular, cell walls contain cellulose c) Eukaryotic, Nucleus, membrane bound organelles, starch stored in plastids 2. A generalized View of a Plant Lifecyle a) Alternating generations between a sporophyte which is a diploid spore producing generation and a gametophyte which is a haploid gamete producing plant b) All modern plants are heteromorphic- their sporophyte and gametophyte generations differ in morphology c) One main trend in evolution of plants is toward a reduction of the haploid generation and the dominance of the diploid generation Plant Life Cycle: Lower plants have a dominant gametophyte generation while higher plants have a dominant sporophyte generation Sperm Gametophyte Generation Haploid In Water Egg Spores Sporophyte Generation Diploid Zygote B. Major Events in Plant Evolution Evolution of Land Plants 1. Non-vascular plants evolved from green algae. Therefore, nonvascular plants must have adaptations that allow waterdwelling algae to overcome the problems of living on land and to best utilize the resources available there. What is going on? What problems do these plants face on land? Which group has an advantage over the other group? Why? Plant Group 2 Plant Group 1 Does plant group #3 have an advantage over groups 1 & 2? If so, what is it? Plant Group 3 Group 2 Group 1 What advantages does plant group #4 have over the other plants? Plant Group 4 Group 3 Group 2 Group 1 All lower plants (groups 1-4) have a significant gametophyte generation. That’s right, they reproduce like animals using sperm and egg! How do sperm travel to the egg? Water of course! Therefore, these plants must be located near water or inhabit areas with abundant rainfall. Group 3 Group 2 Group 1 Plant Group 4 Pollen How do higher plants assure that their gametes reach their significant other even when they live in dry areas? 2. Moving onto land caused plant cells to dehydrate and the following structures evolved to reduce water loss a) Cuticle- waxy layer that prevents evaporation from plant tissues above ground b) Stomata- openings through the waxy layer that allows gas exchange c) Gametangia- protective jacket of cells that prevent the gamete from dehydrating d) Rhizoids- epidermal cells with elongated regions to anchor the plant and provide surface area for water absorption e) Lignin- material embedded in cellulose to strengthen it Major Events in Plant Evolution 3. Development of vascular tissues- tissues that conduct water and minerals allowed plants to grow tall a) Xylem- dead cells that conduct water b) Phloem- living cells that conduct sugars, amino acids and other nutrients 4. Reduced gametophyte generation allows the sporophyte to protect the gametophyte from drought, UV radiation and provide it with nutrients Major Events in Plant Evolution 5. Production of pollen allows the male gametophyte to be protected by a tough coat of cells and can transport the sperm though the air. Pollen replaced swimming sperm 6. Origin of the seed- plant embryo packaged with nutrients. 7. The emergence of Angiosperms- flowing plants that have protective coats on their seeds and reproductive organs that aid pollination II. Classification of the Plant Kingdom Multicellular, Eukaryotic and Autotrophic Algae Bryophytes Water Dwelling Land dwelling mosses, liverworts, hornworts Tracheophytes Have Vascular tissue Lack vascular tissue Seedless Seed Producing Seedless Tracheophytes Psilophyta: Sphenophyta: Lycophyta: Pterophyta: Lack roots Lack roots and Lack roots and (have rhizoids), have small leaf- have small leafand have no like structures like structures leaves. Ex. called microphyls. called microphyls Whisk ferns Ex. Horse tails Ex. Clubmosses have fronds (macrophyls) and rhizomes (underground stem modified for water absorption) Ex. Fern Seed Producing Vascular Plants Gymnosperms: Have true Angiosperms: True roots, roots, stems, leaves, pollen and seeds without a seed coat. Ex. Conifers and Evergreens stems, leaves, flowers, fruits and seeds with seed coats. Ex. Flowering Plants