* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download General Plant Life Cycle
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
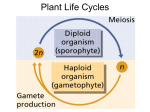
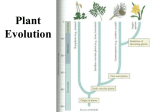
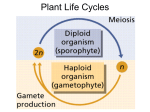
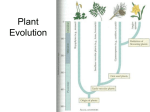
Plant Life Cycles Plant Evolution • Descendants from green algae (~450mya) – Contain cellulose in cell walls – Contain chlorophyll – Starch stored • Land Plants Must Overcome – Drying out – Gas exchange – Nutrient transport system – Support Land adaptations • Cuticle: Waxy coating prevents water loss • Stomata: pores that open/close to permit gas exchange • Roots & Stems: support • Vascular system: tissue that transports nutrients – Nutrients & water go up plant – Sugars go down the plant General Plant Life Cycle • Alternation of generations • Gametophyte (haploid) – Begins with spores created by meiosis – Mature gametophyte grows by mitosis – Male & female organs – Sperm & egg created General Plant Life Cycle • Sporophyte (diploid) – Begins when sperm fertilizes egg (zygote) – Zygote divide by mitosis to create a mature sporophyte – Meiosis produces haploid cells Mosses • Nonvascular, seedless • Grow low to ground to retain moisture • Lack true leaves – Leaf-like structures only 1 cell thick • Rhizoids anchor into soil • Early inhabitant of new ecosystems (succession) Moss Life Cycle • Gametophyte phase – Dominant stage – Carpet of moss growing near ground – Male sperm & female egg created – Sperm swims through water to fertilize egg • Sporophyte phase – Stalk grows up from the gametophyte – Sporangia houses haploid spores – Spores land and new gametophyte grows Ferns • Seedless, vascular plants – Vascular: allows taller growth • Rhizoids: underground stems draw nutrients • Fronds: leaves uncurl – sporangia on underside • Sori: sporangia Fern Life Cycle • Sporophyte phase – Dominant stage – Sporangia produces haploid spores – Spores released into air • Gametophyte phase – Spore grows into prothallus • Archegonium: produces female egg • Antheridium: produces male sperm – Sperm swims to egg – Zygote begins sporophyte stage Conifers • Seed advantages – Don’t depend on water – Protects & nourishes embryo – Allow plants to grow in new locations • Conifers: woody cone houses seeds – Male cones: produce pollen – Female cones: produce egg • Pines, redwoods, spruce, cedar Conifer Life Cycle • Sporophyte phase – Cones grow on tree – Female cones • Megaspores inside (gametophyte) • Male pollen lands – Male cones • Microspores (gametophyte) released & sticks to archegonium • Pollen tube grows from pollen • Sperm travels down pollen tube female male