* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sexual Reproduction of the Flowering Plant
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
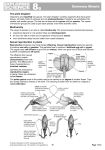
Happy Thursday! Please do the following: • pick up the handouts • pick up glue & a highlighter • have out your notebook Reproduction in Bacteria, Plants and Animals Types of Reproduction: ASEXUAL: Asexual reproduction involves a single cell dividing to make 2 new, identical daughter cells Examples: Mitosis, binary fission, and budding SEXUAL: Sexual reproduction involves two cells (egg & sperm) joining to make a new cell (zygote) that is NOT identical to the original cells Example: Meiosis Asexual Reproduction in Bacteria Prokaryotes such as bacteria divide into 2 identical cells by the process of binary fission Parent cell Chromosome replicates Cell splits 2 identical daughter cells Sexual Reproduction of the Flowering Plant Structure of the flower Function of floral parts Sepal : To protect the flower (and to prevent it from drying out Petals : To attract insects to the flower for pollination Function of floral parts Stamen : To produce the pollen grains in the anthers. (Each pollen grain produces two male gametes/sperm, one of which can fertilize an egg cell) Function of floral parts -Stamen Anther • Produces pollen Filament • Holds the anther in place Function of floral parts Pistil : To produce the ovules (Each ovule contains an egg cell inside an embryo sac) Function of floral parts - Pistil Stigma • Where pollen lands after pollination Style • Pollen travels down this Ovary • Contains ovules (eggs) Pollination Transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of a flower of the same species Pollination Self pollination Cross pollination • Transfer of pollen from an anther to a stigma of the same plant • Transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of a different plant of the same species Animal (insect) pollination Petals brightly colored, scented with nectar Small amounts of sticky pollen Anthers inside petals Stigmas sticky, inside petals Wind pollination Petals small, not colored brightly Anthers outside petals Stigmas large, feathery and outside petals Pollen large numbers, light, dry and small Fertilization Fertilization is the fusion of the male (n) and female (n) gametes to produce a zygote (2n) The pollen grain produces the male gametes Embryo sac produces an egg cell Seed Formation in Flowering Plants • Sperm + Egg Zygote • The zygote grows repeatedly by mitosis to form an embryo which is found within a seed Fruit Formation The ovule becomes the seed The ovary becomes the fruit Fruit Formation A fruit is a mature ovary that may contain seeds The process of fruit formation is stimulated by growth regulators produced by the seeds Fruit and Seed Dispersal Need for dispersal Minimizes competition for light, water etc. Avoids overcrowding Colonizes new areas Increases chances of survival Types of Dispersal 1. 2. 3. 4. Wind Water Animal Self Germination The re-growth of the embryo after a period of dormancy, if the environmental conditions are suitable Water Oxygen Suitable temperature Events in germination cease when the plants leaves have developed and the plant has started to photosynthesize Review of the stages of sexual reproduction in plants… 4 Asexual Reproduction in Plants Asexual reproduction Does not involve gametes, flowers, seeds or fruits examples: binary fission, fragmentation, spore formation and budding It involves only one parent and offspring are genetically identical (have the same genetic content) to the parent So what happens? Part of the plant becomes separated from the parent plant and divides by mitosis to grow into a new plant Plant Reproduction via Spores Spore - a reproductive cell capable of developing into a new individual without fusion with another reproductive cell Spores are different than seeds, they do not contain plant embryos or food stores A structure called sporangia produce the very tiny spores When the sporangia break open, the spores are released and dispersed by water or wind…if the spore lands in a suitable environment, it can grow into a tiny plant Found in non-seed bearing plants such as mosses, algaes, and ferns Sexual Reproduction in Animals (Humans) Fertilization: the fusion of two haploid gametes (sperm and egg) forms a diploid zygote One set of chromosomes from mom combines with one set of chromosomes from dad to create a complete set of chromosomes The zygote is a unique genetic mixture of both parents. Male and Female Reproductive Systems Male Reproductive System Testes – gamete-producing organs Sperm travel from testes to the vas deferens and into the urethra Female Reproductive System Ovaries – gamete-producing organs Ovum (mature egg) moves from an ovary into a fallopian tube Takes about 3-4 days to travel through the fallopian tube – if the ovum is not fertilized within 24-48 hours it dies If fertilization occurs, the fertilized ovum (embryo) develops in the uterus where it is provided nutritional support