* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
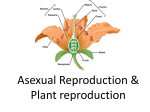
Download Unit B: Topic 3 PLANT REPRODUCTION AND BREEDING Asexual
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
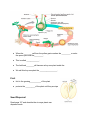
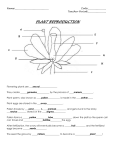
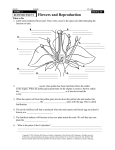
Unit B: Topic 3 PLANT REPRODUCTION AND BREEDING ● people ________ plants to meet their __________ ● selective __________ is choosing specific plants for their special ______________ ● the plants are ____________and their offspring inherit the ____________ of both parents. ● ____________can change plants by going inside the plant ________and changing some of the _____________material ● the parts of the plant that control the ____________is the ______________ Asexual Reproduction ● one __________ plant grows new plants from its_______________, stems or leaves. ● the young plant is ____________ to the parent. There are three methods of asexual reproduction. 1. Layering ● produces plants from the _____________ ● branch from the parent _________to the ground and covers with soil then grows ___________________ 2. Grafting ● a branch from one _______and attaching it to another tree. 3. Cuttings ● cut a small section of a ______or stem to grow a new___________ Sexual Reproduction ● involves _______parent that produce____________ ● plants are slightly ______________ from the parents ● reproduce using ______________ ● helps _____________ adapt to changes Cone Bearing Plants ● female________ contain ovule (_______) ● ___________cone has pollen (sperm) ● pollen blows in the wind to__________ cone ● egg is fertilized and seed is formed in the cone Flowering Plants Pollination ● Pollination occurs when pollen has been__________ from the anther to the_________. ● When the pollen grain _________________ on the stigma it creates a ________called the pollen ________ as it travels toward the __________. ● When the ________ cell from the pollen grain reaches the _________ or ovule the sperm joins with the_________. ● This is called _____________. ● The fertilized ________will become a tiny new plant inside the. ● We call this tiny new plant the __________________. Fruit ● fruit is the growing___________ of the plant ● protects the __________of the plant until they are ripe Seed Dispersal Read page 127 and describe the six ways plants can disperse seeds. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Germination ● the ____________of the seed into a ____________.