* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Reproduction sexual reproduction involve two parents
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
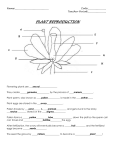
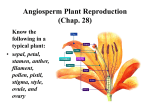
Review: meiosis vs mitosis oogenesis and spermatogenesis differences between sperm and egg Nov 99:35 AM Types of Reproduction sexual reproduction involve two parents producing two haploid gametes which combine to produce an offspring asexual reproduction involves one parent who produces a diploid gamete which will develop into an adult (an exact copy) there are various types of asexual reproduction (see handout provided) Nov 99:36 AM 1 Reproductive Structures in Angiosperms (flowering plants) see diagram on page 176 (a) Pistil: Female reproductive part including the ovary, style and stigma. (b) Stamen: Male reproductive part including filament and anther. (c) Pollen: Powdery material consisting of pollen grains produced by the anther. Carried by wind and insects to other plants for fertilization.(contains sperm) (d) Ovules: Tiny structures in a seed plant containing the embryo sac that develop into seeds after fertilization (e) Seed: Reproductive structure of a plant made up on an embryo, stored food and a tough waterproof coat (f) Fruit: The ripened body of a seed plant Nov 99:49 AM Nov 910:08 AM 2 Sexual Reproduction in Plants: (1) Pollen is produced in the anther and is distributed by wind, insects, etc (2) The pollen will attach itself to the sticky stigma of another plant pollen contains: (a) generative nucleus which produces 2 sperm nuclei (b) tube nucleus which produces a pollen tube (3) Sperm nuclei travel down the pollen tube created in the style down to the ovule (4) One sperm nucleus (n) joins with an egg (n) to form a diploid zygote (2n) Nov 910:14 AM (5) The other sperm nucleus unites with 2 haploid polar nuclei to produce a triploid endosperm (3n) (6) The endosperm becomes the food for the embryo to remain viable until germination (7) The embryo is protected by a hard seed case created around the fertilized egg (8) The ovary swells around the seed to protect it. Swollen ovary is called fruit NOTE: When fruit is eaten by wild animals the seeds pass through the digestive system and exit with the feces. In this way seeds are spread and germinate in various places Plant reproduction Nov 910:18 AM 3 Readings: Pages 174 181 Questions: Page 181: #'s 6,8 Nov 910:22 AM 4