* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PlantReproduction
Animal sexual behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Parental investment wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Parthenogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
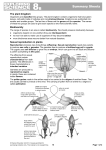
Asexual Reproduction & Plant reproduction Asexual & Sexual Reproduction • Sexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically different from their parents. • Asexual reproduction produces offspring genetically identical to their parent. • Examples: 1. Binary Fission 2. Budding 3. Spore Production 4. Fragmentation 5. Parthenogenesis Modes of Reproduction Asexual Reproduction • One parent cell divides by mitosis to produce 2 identical cells that are clones of the parent Types of Asexual Reproduction 1. Budding - an outgrowth on the parent organism that develops into a new organism that eventually separates from the parent. • Example-yeast and hydra http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=489CSop00sY 2. Binary fission –DNA is copied through mitosis, causing the original parent cell to split into two smaller, genetically identical cells. Example-bacteria http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D Y9DNWcqxI4 3. Spore production - spores are produced by mitosis and are released from the original parent cell for dispersal. • Example – Fungi (Rhizopus stolonifera) http://bcs.whfreeman.com /thelifewire8e/content/cat _010/30040.html 4. Fragmentation – when a piece of the parent organism breaks off and is dispersed. Each section is able to form a new organism. • Example - House plants formed from cuttings Planaria flatworm 5. Parthenogenesis – when offspring are produced from unfertilized eggs • Example - some insects, such as the Oleander aphid Sexual Reproduction • In sexual reproduction new individuals are produced by the fusion of haploid gametes to form a diploid zygote. • Sexual reproduction offers the benefit of generating genetic variation among offspring, which enhances the chances of the population's survival. Sexual Reproduction in Angiosperms Parts of the flower Pistil: The ovule producing part of a flower. Stigma: the sticky surface at the top of the pistil; it traps and holds the pollen. Style: the tube-like structure that holds up the stigma. Ovary: where ovules are produced Ovule: The female gamete (i.e. Egg) Stamen: The pollen producing part of a flower Anther: The part of the stamen where pollen is produced. Filament: thread-like part that holds up the anther Pollen: the male gamete (i.e. sperm) Fruit - the mature ovary Seed - the mature ovule Life Cycle of Flowering Plants 1. Pollination – Pollen is transferred from the anther to the stigma – Two types: i. Self-pollination: occurs within the same flower, or between flowers on the same plant ii. Cross-pollination: Occurs between flowers on different plants 2. Fertilization – Pollen tube grows down through the style to deliver sperm nucleus to the egg – Egg and sperm unite to form a zygote 3. Seed Development – Zygote grows and develops into an embryo plant – Ovule wall thickens to become a seed coat – Seed also contains stored food for the developing embryo 4. Fruit Development – Ovary tissue develops to enclose the seeds – This is called the fruit (ex: apple, tomato, green pepper – Aids in seed dispersal http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RuYrFwDuYn0 What is found in a pollen grain? 1. A generative nucleus which divides to produce two sperm nuclei 2. A tube nucleus which causes the pollen tube to grow What is found in an ovule? • The ovule contains: 1. One Egg 2. Two polar bodies What is double fertilization? • When the pollen tube enters an ovule: – one sperm nucleus fuses with an egg to form the zygote (2n) – the other combines with two polar nuclei to form the endosperm (3n) - a food reserve • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gq8NWh98wQs