* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Seed Plants - Biology Department
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
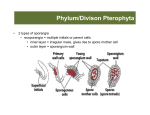
Seed Plants BSC 2011L Seed Vascular Plants Among plants, these include the gymnosperms and angiosperms Reproductive differences in seedless vs. seed plants Sporangia Protection of egg Non- seed plants utilize an archegonium on the gametophyte to protect egg, sporophyte develops within archegonium Seed plants protect entire gametophyte within ovule (which will develop into seed) Transport of male gametophytes Seed plants have 2 types: megasporangium, microsporangium Non-seed plants – use water for flagellated sperm Seed plants – male gametophyte carried by wind (pollen) Sporophyte vs. gametophyte Non-seed – sporophyte dependent on gametophyte Seed – gametophyte dependent on sporophyte Plant Taxonomy, continued Refer to previous PowerPoint for Seedless plant taxonomy Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae Phylum Cycadophyta Phylum Ginkgophyta Phylum Gnetophyta Phylum Coniferophyta Phylum Anthophyta Class Eudicots Class Monocots Cycads Ginkgos Gnetophyta Conifers Flowering Plants Dicots Monocots Gymnosperms “Naked Seed” Ovules and seeds of gymnosperm are exposed on cone scale Microsporangia and megasporangia located on different cones, sometimes different plants Female cones are larger than male cones Gymnosperms Cycads Cone-bearing, palmlike plants found mainly in tropical and subtropical regions Gymnosperms Ginkgos Only 1 species survives today Usually only male trees are used since female trees produce smelly seeds Gymnosperms Gnetophytes Can grow as shrubs, trees, or vines Gymnosperms Conifers Largest group of gymnosperms Evergreens – pines, hemlocks, spruces Nonevergreens – cypress tree Gymnosperms Pine life cycle Gymnosperms Pine Cone Female Male – small “dots” are pollen Angiosperms Dominant plants today “Flowering Plants” Microsporangia and Megasporangia located on same flower Double Fertilization Mature pollen grain contains 2 sperm 1 fertilizes egg Other joins 2 polar nuclei to form endosperm (food for embryo) Angiosperms Monocots vs. Dicots Quiz yourself Angiosperms Life Cycle Angiosperms Seed Germination Angiosperms Fruits Develops from ovary Ovary wall thickens to be pericarp 3 layers Exocarp – skin of fruit Mesocarp – fleshy part Endocarp – boundary around seed Review Dichotomous key on page 287 • Angiosperms Fruits • Simple Fruits (develop from single ovary) • Aggregate Fruits (develop from numerous ovaries within a single flower) • Blackberries • Raspberries • Strawberries • Multiple fruits (develop from a number of ovaries of several flowers) • Pineapples • Mulberries • Figs Fleshy fruits • • • • Drupes – cherry Berries – grape, tomato Pomes – apple Dry fruits • • • • • • Legumes – pea Samaras – maple Nuts – oak, walnut Grains – wheat, corn Achenes -- sunflower, dandelion