* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Life Science-Plants Part 2 of 2
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
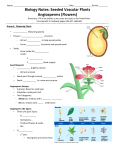
Life Science-Plants Part 2 of 2 Mrs. Delaup V. Martinez Ms. Abney Elementary 1. What are the two types of plants that form seeds? • There are two kinds of plants that form seeds: cone-bearing plants and flowering plants. 2. ____ are found in cones of cone bearing plants and the fruit of the flowering plants? • Seeds are found in the cones of conebearing plants and the fruit of flowering plants. 3. What are reproductive structures of plants? • Flowers are reproductive structures of plants. 4. What is the part of a flowering plant that contains and protects the seeds? • A fruit is the part of a flowering plant that contains and protects the seeds. 5. What are the three main parts of a flower? • Flowers have parts that work together to make seeds: stamen, pistil, and sepal 6. What does the stamen do? • The stamen makes pollen. 7. What part of the plant collects pollen ? • The pistil collects the pollen. • The bottom of the pistil is the ovary where seeds form. • The pistil is the central structure of the flower. It is surrounded by the stamens, the petals, and the sepals. 8. What are leaf like petals at the base of the flower? • Sepals are leaf like petals at the base of a flower. 9. When do seeds form? • Seeds form after a flower is pollinated. 10. What happens when pollen is carried from a stamen to a pistil? • Pollination happens when pollen is carried from a stamen to a pistil by wind or animals. 11. What is the name of the young plant inside of a seed? • A seed is made up of a young plant, called an embryo. 12. What does the seed do when its needs have been met? • When the seed has met its needs it germinates, or sprouts. 13.Where do the seeds of a pine tree form? • The seeds of a pine tree (a cone-bearing plant) form between the scales of its cones. 14.Do all plants grow from seeds? • Not all plants grow from seeds. 15. Give an example of a plant that does not grow from a seed. • Some plants grow from a piece of stem put into water. New roots grow from the bottom of the stem. The new stem with roots is planted in soil. 16. What plant part is a potato? • Potatoes are tubers, or swollen underground stems. Tubers are often dug up to eat. 17. List three examples of how plants have adaptations that help them survive in different environments. • Plants have many adaptations that help them survive in different environments. 17. An example of a plant adaptation: • The ___________ is an unusual plant because it gets nutrients from insects that land on its leaves. • Venus Fly Trap 17. An example of a plant adaptation. • During the winter months there is less daylight for photosynthesis. Therefore, some trees enter a state of _______ • , or lower activity until spring. • Dormancy 17. Example of a plant adaptation: • C. Cacti have roots that grow near the surface because it is easier to collect _________ in their very dry climate. • Rain water