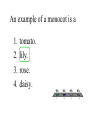* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
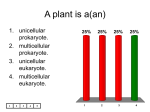
Biology Ch. 22 Review A plant is a(an) 1. unicellular prokaryote. 2. multicellular prokaryote. 3. unicellular eukaryote. 4. multicellular eukaryote. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of all plants? 1. 2. 3. 4. are eukaryotic have cell walls produce seeds are multicellular 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 To produce spores, all plants must undergo 1. 2. 3. 4. mitosis. meiosis. fertilization. asexual reproduction. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Plants use the energy of sunlight to 1. exchange gases with the atmosphere. 2. take in water from the soil. 3. carry out cellular respiration. 4. carry out photosynthesis. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Without gas exchange, a plant would be unable to 1. 2. 3. 4. make food. absorb sunlight. make minerals. absorb water from the soil. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Which of the following is NOT true? 1. Plants have adaptations that maximize light absorption. 2. Plants require more water on a sunny day. 3. Plants get the water they need from the atmosphere. 4. Plants can lose water while exchanging gases with the atmosphere. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 The first plants evolved from 1. mosses. 2. an organism similar to multicellular green algae. 3. a protist that lived on land. 4. photosynthetic prokaryotes. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Living on land required that plants 1. evolve photosynthetic pigments. 2. conserve water. 3. exchange gases. 4. have cell walls. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Without plants, 1. animals could not live on land. 2. there would be no green algae in the oceans. 3. animals could not undergo cellular respiration. 4. there would be no carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Which of the following statements is true about bryophytes? 1. They have specialized tissues that conduct water. 2. They draw up water by osmosis. 3. They are not highly dependent on water. 4. They are a group of plants made up of algae and mosses. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Bryophytes need standing water to 1. reproduce. 2. draw up water by osmosis. 3. undergo photosynthesis. 4. grow tall. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Because bryophytes do not have vascular tissue, they 1. do not conduct water. 2. grow close to the ground. 3. can draw up water only a few centimeters above the ground. 4. all of the above 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 In liverworts, the structures that produce eggs and sperm look like 1. 2. 3. 4. fronds. horns. liver. tiny green umbrellas. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Which one of the following structures has functions similar to that of roots? 1. 2. 3. 4. gemma rhizoid capsule stalk 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Which of the following is NOT true about mosses? 1. They are the most common bryophytes. 2. Long, thin cells called gemmae anchor them in the ground. 3. They are the most abundant plants in polar regions. 4. Some mosses form clumps of gametophytes growing together. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 What is the sperm-producing structure of a bryophyte? 1. 2. 3. 4. gemma archegonium rhizoid antheridium 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Which of the following is LEAST related to the others? 1. 2. 3. 4. protonema sporophyte gametophyte rhizoid 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 In bryophytes, haploid reproductive cells are produced by the 1. haploid stage. 2. diploid stage. 3. gametophyte and sporophyte. 4. all of the above 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Which of the following includes all the others? 1. 2. 3. 4. xylem vascular tissue phloem tracheids 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Xylem and phloem are NOT 1. conducting tissues. 2. vascular tissues. 3. present in bryophytes. 4. present in ferns. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Xylem tissue is important to ferns because it 1. can conduct water over long distances. 2. allows water to diffuse into the roots. 3. carries carbohydrates to all parts of the plant. 4. allows ferns to reproduce in dry environments. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Club mosses are 1. nonvascular plants. 2. seed plants. 3. seedless vascular plants. 4. none of the above 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Horsetails do NOT 1. have xylem tissue. 2. produce seeds. 3. have roots. 4. have phloem tissue. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Which of the following statements is true? 1. Ferns can thrive in areas with little light. 2. Unlike club mosses, ferns grow in moist environments. 3. Fern fronds grow from the plant’s roots. 4. The leaves of Equisetum lack bundles of vascular tissue. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 1. 2. 3. 4. Fern spores are produced by the gametophyte. produced in the rhizomes. called sori. 0% produced in sporangia. 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Which of the following structures in ferns is diploid? 1. 2. 3. 4. gametophyte sporangium egg spore 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 How is the fern life cycle different from the moss life cycle? 1. A fern gametophyte always has both archegonia and antheridia. 2. The young gametophyte is haploid. 3. The mature sporophyte is diploid. 0% 0% 0% 0% 4. The mature sporophyte grows from the gametophyte. 1 2 3 4 Which of the following includes a plant embryo, a food supply, and a protective covering? 1. 2. 3. 4. pollen grain spore seed gametophyte 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Seed-bearing plants differ from all other plants in that 1. they have vascular tissue. 2. they do not have a gametophyte generation. 3. their gametes do not require water for fertilization to occur. 4. all of the above 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 The gametophytes of gymnosperms are found inside reproductive structures called 1. 2. 3. 4. flowers. cones. embryos. angiosperms. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 When land environments became drier millions of years ago, 1. many moss and fern species became extinct. 2. mosses evolved vascular tissue. 3. mosses and ferns no longer required water for reproduction. 4. many angiosperm species 0% became extinct. 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 The most ancient surviving seed plants are the 1. 2. 3. 4. mosses. liverworts. ferns. gymnosperms. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Which of the following statements is NOT true? 1. Seed plants can coexist with seedless plants. 2. The evolution of seed plants caused many species of mosses and ferns to become extinct. 3. Early seed plants were successful because they were adapted to dry environments. 4. Fossils of seed-bearing plants exist from almost 360 million years ago. 0% 0% 0% 0% 1 2 3 4 The four groups of gymnosperms are conifers, cycads, ginkgoes, and 1. 2. 3. 4. bryophytes. horsetails. liverworts. gnetophytes. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Which gymnosperms produce exposed seeds? 1. conifers only 2. conifers and cycads only 3. conifers and ginkgoes only 4. conifers, cycads, gnetophytes, and ginkgoes 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 There is evidence that Ginkgo biloba 1. was the first gymnosperm to have evolved. 2. evolved before most other living species of seed plants. 3. evolved from an angiosperm. 4. has characteristics that differ greatly from its ancestors. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Angiosperms produce seeds inside protective structures called 1. 2. 3. 4. pollen grains. cones. ovaries. petals. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Which term below is least closely related to the others? 1. 2. 3. 4. fruit seed ovary cone 0% 1 0% 2 0% 3 0% 4 The specialized reproductive structure that evolved most recently is the 1. 2. 3. 4. seed. pollen grain. ovary. gametophyte. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 An example of a monocot is a 1. 2. 3. 4. tomato. lily. rose. daisy. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 The number of seed leaves distinguishes 1. club mosses from mosses. 2. angiosperms from gymnosperms. 3. two classes of angiosperms. 4. seed plants from seedless plants. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Unlike a dicot, a monocot has 1. four or five petals per flower. 2. two cotyledons. 3. taproots. 4. parallel leaf veins. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Flowering plants that complete a life cycle within a single growing season are called 1. 2. 3. 4. annuals. dicots. perennials. monocots. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Which type of plant lives the longest? 1. 2. 3. 4. annual biennial perennial none of the above 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Which of the following statements is NOT true? 1. The roots of a perennial do not die at the end of the growing season. 2. A biennial is smaller during its second growing season. 3. The stems of some perennials die at the end of the growing season. 4. A biennial flowers only once. 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 If an organism is multicellular, it cannot be a plant. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 Losing excessive amounts of water through evaporation may affect a plant’s ability to carry out photosynthesis. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 The figure shows the evolutionary relationship of the major plant groups living on Earth today. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 Bryophytes are low-growing because they lack vascular tissue. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 Bryophytes include ferns, liverworts, and hornworts. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 Having archegonia and antheridia located on the same moss plant would help ensure fertilization. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 Xylem tissue transports solutions of nutrients and carbohydrates produced by photosynthesis. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 The thick cell walls of tracheids prevent the cells from bulging when water moves through them. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 Tracheids extend from the roots to the leaves of a club moss. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 A frond is part of a fern’s haploid stage. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 The most important adaptation that enabled the ancestors of gymnosperms and angiosperms to live in dry environments was the spore. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 Welwitschia is a gnetophyte that lives in the desert. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 Unique reproductive features commonly known as flowers are characteristic of gymnosperms. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 If a seed has two cotyledons, it will have fibrous roots. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 Biennials are pollinated during their first year of growth. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2