* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download G163S10L15_enso_ROD
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Southern Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Ocean wikipedia , lookup
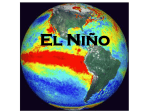
El Niño/Southern Oscillation • Major climatic perturbation on the planet • Coupled atmosphere ocean process • Key is the western tropical Pacific – Ascending branch of the Walker circulation – Potential energy for Kelvin wave pulse • www.pmel.noaa.gov/tao/elnino/nino-home.html The Southern Oscillation • Discovered in 1928 by Sir Gilbert Walker • Links D’s in global climate indices • Proposes a zonal circulation cell over the equatorial Pacific The Southern Oscillation The Southern Oscillation • Pressure D’s regulate strength of the trades • El Niño periods = weak trades Southern Oscillation Index • SOI = Tahiti - Darwin air pressure D’s • Low SOI = El Niño conditions Southern Oscillation Nino Regions Multivariate ENSO Index • Combines observations of air pressure, zonal & meridional components of wind, sea surface temperature, air temperature and total cloudiness. • Positive MEI = ENSO conditions Walker Circulation • East-to-west pressure gradients drive trades Walker Circulation • Vertical cell driven by warmest waters Western Pacific Warm Pool Coupled Walker/Ocean Circulation Coupled Walker/Ocean Circulation El Niño Events • Relaxation of trades causes warm pool to slosh across Pacific basin El Niño Conditions El Niño Conditions La Nina • Opposite phase of the ENSO cycle • Intensified trades & Walker circulation • Thermocline undergoes maximum upwelling EL NIÑO/SOUTHERN OSCILLATION (ENSO) DIAGNOSTIC DISCUSSION issued by CLIMATE PREDICTION CENTER/NCEP 10 May 2010 A transition from El Niño to ENSO-neutral is underway. Sea surface temperatures are decreasing across much of the Pacific Ocean. Based on current observations and dynamical model forecasts, a transition to ENSO-neutral conditions is expected by June 2010, which will continue into the Northern Hemisphere summer 2010. Although most models predict ENSO-neutral conditions, there is a growing possibility of La Niña developing during the second half of 2010. Today… Today… Altimetry & ENSO States • Most “action” is in the tropical Pacific • Effects are seen in other places – East subtropics – Western NECC region Effects of an El Niño • Region of ascending air has moved to center of equatorial Pacific • Climate system shifts over 10,000 km to east • Affects the entire planet An El Niño History • late 1800s Fishermen name El Niño to the periodic warm waters that appear off the coasts of Peru and Ecuador around Christmas. • 1928 Gilbert Walker describes the Southern Oscillation. • 1957 A large El Niño is observed which affects not just the coasts of Peru and Ecuador but the entire Pacific Ocean. • 1969 Jacob Bjerknes links the Southern Oscillation with El Niño events. An El Niño History • 1975 Wyrtki uses island sea level to show how eastward flow causes SST’s to rise in east Pacific. • 1976 An idealized computer model demonstrates that winds over the far western Pacific can change SST off Peru. • 1982 A severe El Niño develops unexpectedly, but is recorded in detail with newly developed ocean buoys. • 1985 Several nations launch the Tropical OceanGlobal Atmosphere (TOGA) program. An El Niño History • 1986 First coupled model of ocean & atmosphere predicts El Niño event. • 1988 Researchers explain how the "memory" of the ocean--the lag between a change in the winds and the response of the ocean--influences terminations of El Niño and the onset of La Niña. • 1996-1997 The array of instruments monitoring the Pacific, plus coupled ocean-atmosphere models, enable scientists to warn the public of an impending El Niño event. Coupled Walker/Ocean Circulation El Niño Conditions Effects of an El Niño • Places that were wet are now dry and vice versa Effects of an El Niño El Niño in Australia El Niño in Australia Teleconnections • Discovered in 1928 by Sir Gilbert Walker • Links D’s in global climate indices • Proposes a zonal circulation cell over the equatorial Pacific El Niño • Hadley cells intensify as source of heat is now in central equatorial Pacific • Jet stream intensifies & takes south path El Niño in the United States El Niño in the United States El Niño in the United States El Niño in the United States El Niño & Hurricane Damage El Niño & Hurricane Damage El Niño & Diseases Delayed Oscillator Theory • Seeds of El Nino destruction as it starts... Delayed Oscillator Theory Delayed Oscillator Theory El Niño Conditions 97-98 El Niño Event 97/98 El Niño • At its peak, the 97/98 El Niño was biggest of all time 97/98 El Niño 97/98 El Niño 97/98 El Niño • TOPEX/Poseidon sea level anomaly December 1, 1997 97/98 El Niño 97/98 El Niño OLR = outgoing longwave energy (high OLR = no clouds) 97/98 El Niño 97/98 El Niño Movie More readings • NOAA ENSO Page www.pmel.noaa.gov/tao/elnino/nino-home.html • Review of 97/98 El Nino www.icess.ucsb.edu/~davey/Geog163/950.pdf