* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
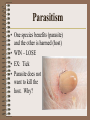
ECOLOGY The Study of the Interaction of organisms with their environment The Environment • Biotic Factors all of the living things in the environment • Abiotic Factors all of the nonliving things in the environment Community • All of the living things in an area that DEPEND on each other Relationships in a Community -1 Symbiosis = “Living Together” – Close relationship between two or more species – Examples • Mutualism • Commensalism • Parasitism Mutualism • Both species benefit from the relationship • WIN – WIN • EX: acacia tree and ants. Commensalism • One species benefits from the relationship and the other is unaffected. • WIN – “I don’t care” • EX: Orchid Parasitism • One species benefits (parasite) and the other is harmed (host) • WIN – LOSE • EX: Tick • Parasite does not want to kill the host. Why? Relationships in a Community - 2 • Predation - The feeding of one organisms on another – Predator • hunts/eats – Prey • gets eaten Habitat • The Place where an organism lives Niche • The JOB of an organism in a community Niches in a Community • PRODUCER • CONSUMER • DECOMPOSER Producer (Autotroph) • Plants make food in a community • Photosynthesis – using sunlight to make food Consumer (Heterotroph) • Can’t make their own food • Primary Consumer Eats plants • Secondary Consumer Eats other animals Decomposers • Are consumers • Get food by breaking down dead matter • Recycle nutrients • Examples – Fungi (molds, mushrooms) – Bacteria Energy • The ability to do work • Flows through an ecosystem • What is the primary source of energy in an ecosystem? The Sun Food Chain • Pathway of energy through an ecosystem Sun Grass Producer Grasshopper Primary Consumer Bird Secondary Consumer Food Web • Food chains connected in a community • All of the possible feeding relationships Food Web Energy Pyramid TERTIARY CONSUMER SECONDARY CONSUMER PRIMARY CONSUMER PRODUCER Energy Pyramid • Shows energy loss in a food chain – 90% lost as heat • # of organisms at each level decreases – Less energy available • Because of energy loss, maximum of 5 levels.