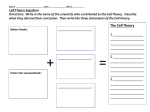
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Basic Ecology Powerpoint BasicEcologyFIB-PPModified
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
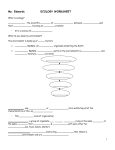
Ecology Part1-WHAT IS ECOLOGY? Ecology- the scientific study of interactions between organisms and their environments. Ecology is a science of relationships WHAT DO YOU MEAN BY ENVIRONMENT? The environment is made up of two factors: • Biotic factors- all living organisms inhabiting the Earth • Abiotic factors- nonliving parts of the environment (i.e. temperature, soil, light, moisture, air currents) Biome Ecosystem Community Population Organism Biome-regions of the world with similar abiotic factors (climate:weather, temperature) & biotic factors (animals and plants). Examples: Rainforests, Deserts, Oceans. Ecosystem - populations in a community and the abiotic factors with which they interact (ex. marine, terrestrial) Community - several interacting populations that inhabit a common environment and are interdependent. POPULATION a group of organisms of one species living in the same place at the same time that interbreed Produce fertile offspring Compete with each other for resources (food, mates, shelter, etc.) Organism - any unicellular or multicellular form exhibiting all of the characteristics of life, an individual. VIDEO RECAP: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ed KhQVHc3Ao ECOLOGY Part 2: Roles that organisms play within their environment EQ: 1. .What are the different roles that an organism can have in their environment? 2. What kinds of relationships do organisms have with each other? Habitat vs. Niche Niche - the role a species plays in a community; its total way of life Habitat- the place in which an organism lives out its life http://www.youtube.com/watch?v= Q5Vl4V24eNI&list=UU6a7JghQc 25EsD65r5h4Amw Habitat vs. Niche A niche is determined by the tolerance limitations of an organism, or a limiting factor. Limiting factor- any biotic or abiotic factor that restricts the existence of organisms in a specific environment. Habitat vs. Niche Examples of limiting factors •Amount of water •Amount of food •Temperature •Amount of space •Availability of mates Feeding Relationships • There are 3 main types of feeding relationships 1. Producer - Consumer 2. Predator - Prey 3. Parasite - Host Feeding Relationships Producer- all autotrophs (plants), they trap energy from the sun • Bottom of the food chain Feeding Relationships Consumer- all heterotrophs: they ingest other organisms Examples: Herbivores, Carnivores, Omnivores, Decomposers Feeding Relationships Herbivores- eat plants. Carnivores-eat meat • Predators – Hunt prey animals for food. • Scavengers – Feed on carrion, dead animals Feeding Relationships Omnivores -eat both plants and animals Feeding Relationships Decomposers • Breakdown the complex compounds of dead and decaying plants and animals into simpler molecules that can be absorbed Symbiotic Relationships Symbiosis- two species living together 3 Types of symbiosis: 1. Commensalism 2. Parasitism 3. Mutualism Symbiotic Relationships Commensalismone species benefits and the other is neither harmed nor helped Ex1; Plants (epiphytes) on trees. Ehttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M xpa6gPIbLEx. orchids on a tree Symbiotic Relationships CommensalismEx2. polar bears and cyanobacteria Symbiotic Relationships Parasitismone species benefits (parasite) and the other is harmed (host) • Parasite-Host relationship Symbiotic Relationships Parasitism- parasite-host Ex. lampreys, leeches, fleas, ticks, tapeworm http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-SYhOD1Yx10 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aNXYGpxuvNY http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vMG-LWyNcAs Symbiotic Relationships Mutualismbeneficial to both species Ex 1. cleaning birds Symbiotic Relationships Ex2: Cleaner Fish http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TOC2Qc2Qedw http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TOa8y95khK8 Type of Species relationship harmed Commensalism Parasitism Mutualism = 1 species Species benefits Species neutral VIDEO RECAP: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ed KhQVHc3Ao http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zS mL2F1t81Q Trophic Levels EQs: • What are Trophic Levels? • What is the difference between a food chain and a food web? Trophic Levels • Each link in a food chain is known as a trophic level. • Trophic levels represent a feeding step in the transfer of energy and matter in an ecosystem. Trophic Levels Biomass- the amount of Biotic matter in an area. • As you move up a food chain, both available energy and biomass decrease. • Energy is transferred upwards but is diminished with each transfer. E N E R G Y Trophic Levels Tertiary consumers- top carnivores Secondary consumerssmall carnivores Primary consumers- Herbivores Producers- Autotrophs Trophic Levels Food chain- simple model that shows how matter and energy move through an ecosystem Trophic Levels Food web- shows all possible feeding relationships in a community at each trophic level • Represents a network of interconnected food chains Stop and think • Fill in the blanks to create a food chain found in Washington. Food chain (just 1 path of energy) Food web (all possible energy paths) Videos • • • • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cWh-XKhh8xo http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mCHdhXMFhcU http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qUZkWZ12A8s http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YvZlooi5_kE BioGeoChemical Cycles (Nutrient cycles) EQs: 1-How does matter cycle through an ecosystem? 2- What are 3 important biogeochemical cycles? BioGeoChemical Cycles Cycling maintains homeostasis (balance) in the environment. •3 cycles to investigate: 1. Water cycle 2. Carbon cycle 3. Nitrogen cycle 1) Water cycle- Is also known as the hydrologic cycle or the H2O cycle. It describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth Water cycle- It has 4 main steps: •Evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation Water cycle- 2) Carbon cycle- All living things are made of carbon. Carbon is also a part of the ocean, air, and even rocks. Carbon flows between the atmosphere, land, and ocean in a cycle that encompasses nearly all life and sets the thermostat for Earth's climate. Carbon cycle- Photosynthesis, consumption, respiration, and decomposition are the processes that move carbon and through the environment. CARBON CYCLE Carbon Cycle- another example 3) Nitrogen cycleAtmospheric nitrogen (N2) makes up nearly 78%-80% of air. Organisms can not use it in that form. Bacteria converts nitrogen into usable forms, or “fixes” it. Nitrogen cycleNitrogen fixation-When ___________ converts atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into ammonium (NH4+) which can be used to make amino acids which combine to make Proteins. DNA is made of Amino acids and all organisms need proteins for growth and repair. Nitrogen cycle- Nitrogen-fixing bacteria is very important in the nitrogen cycle because it makes nitrogen usable by plants which can then be eaten by animals. Nitrogen Cycle Vidoes • • • • CARBON: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HrIr3xDhQ0E http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2Jp1D1dzxj8 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0Vwa6qtEih8 • • • NITROGEN: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DP24BceOwt8&list=TLOuTH955iE1TqviFC3J_O2bJ8BXRtwmvX http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vypXvv58700 • • • • • WATER: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F9Yi4dAzHsc&list=PL88C2F8D87EC2EAAE http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0_c0ZzZfC8c&list=PL88C2F8D87EC2EAAE&index=3 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=372K0jyO0hQ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UDyPkjQxkas • • ALL: http://www.bozemanscience.com/biogeochemical-cycling Videos en espanol • • Agua: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5QPlLOlJ7a0 • • C, N & P http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DOfI8lQAh98&list=PL8C1FCC26AAD0834D