* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download There`s a Quiz-a
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Conservation agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Decline in amphibian populations wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity of New Caledonia wikipedia , lookup
Conservation biology wikipedia , lookup
Habitat destruction wikipedia , lookup
Tropical rainforest wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Tropical Andes wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
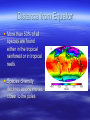
Factors Contributing to Biodiversity Biodiversity Why are there more species in some places than others??? Factors which lead to higher biodiversity Heterogeneity of Habitats: Variety of habitats = higher biodiversity Chugach vs. ANWR Isolation from/access to centers of dispersal Islands and tips of peninsulas (Florida/Baja Mexico) have lower levels of biodiversity Species Area Effect Distance from Equator More than 50% of all species are found either in the tropical rainforest or in tropical reefs Species diversity declines as one moves closer to the poles Plant Productivity Raise in Temp = raise in photosynthesis Greater sun intensity = more photosynthesis More rainfall = more growth Lack of seasonality Plant productivity leads to overall biodiversity More food = more animals (well, duh…) Tropics = complex food web. Fruit & flies > greater # of bats/rodents > greater overall # of spp. Farther from equator = simpler food web Grazers and predators get less return on energy expended Fruit = high in energy Grass = low in energy Meat = high energy, but high energy expended Diverse habitat = high biodiversity Structurally complex habitats (more niches) = high biodiversity (rainforests, deserts) Simple habitats (fewer niches) = low biodiversity (grasslands, marshes, tundra)