* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology - Shaw Communications
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Biosphere 2 wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Deep ecology wikipedia , lookup
Conservation biology wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Marine conservation wikipedia , lookup
Cultural ecology wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
C. Ecology
I. Ecosystems and Communities
Biodiversity
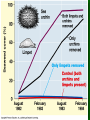
Zebra Mussels
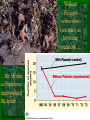
Predator Removal
C
l
i
m
o
g
r
a
p
h
Community Ecology
Interspecific Interactions and Community
Structure
Disturbance and Community Structure
Biogeographic Factors
Competitive Exclusion Hypothesis
Microhabitats of Lizard Species
Anolis distichus –
sunny leaf surface
Anolis insolitus –
shady branch
Deceptive coloration
Camouflage – chick (poorwill); lizard
Aposematic (warning) coloration
Batesian mimicry
– the hawkmoth larva (left) resembles a snake when
disturbed
{harmless resembles harmful}
Mullerian mimicry
– the cuckoo bee (left) and the yellow jacket both
have stingers that release toxins
{both harmful but more exposure to potential
predators of linking markings with harm}
Mutualism –
between acacia trees
and ants
Parasitic Nasonia (wasps)
Commensalism –
one species
benefits, the other
is neither harmed
nor helped
(usually)
Trophic
levels
– terrestrial
and marine
food chains
{make sure your
assignment doesn’t
resemble this one!
;)}
Antarctic
marine food
web
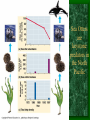
Partial food web
Without
Pisaster
ochraceous
(sea stars) as
keystone
predators…,
…the Mytilus
californianus
monopolized
the space
Sea Otters
are
keystone
predators in
the North
Pacific
A fire on a grassland burns the detritus and
rejuvenates the prairie so that virtually all the
biomass is living a month after a burn (right)
Large disturbances occur more often when small
disturbances are prevented. Lodgepole pine cones
require intense heat to open and germinate.
Soil nitrogen concentration during succession
after a glacial retreat
Forest
community 1 is
more diverse
b/c it has
greater
heterogeneity –
both in species
richness
(number) and
relative
abundance
Species richness
generally
decreases towards
the poles
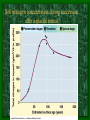
Energy and Species Richness
- annual available energy is measured by evapotranspiration
(combining solar radiation and temperature) and expressed as
rainfall equivalents in mm/yr.
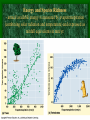
The number of plant
species on the
Galapagos Islands in
relation to the area of
the island.
Ecosystems
Primary Production
Secondary Production
Cycling of Chemical Elements
Human Impact
Energy flow = broken red lines;
Material cycling = solid blue
lines
Energy =
solar radiation chemical
transfers in food web
heat radiated to space
Materials =
pass through trophic levels
detritus back to
primary producers
Fungi decomposing a log
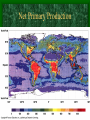
Primary Production
Net Primary Production
II. Biomes
Lake Zonation
Oligotrophic Lake
Eutrophic
Lake
Wetlands
Estuaries
Marine: 1. Tide Zone 2. Coral Reef 3. Benthos
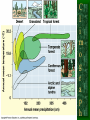
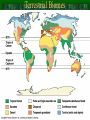
Terrestrial Biomes
Tropical Forests: 1. Highland 2. Lowland 3. Seasonal
Deserts
Tundra
the Biosphere
Behavioral Ecology
Learning
Animal Cognition
Sociobiology
Behavior
Components
Digger Wasp
Behavior
Female Songbird Preferences
Geese Imprinting
Two types of bird-song development
Electronic Surveillance of honeybees
Cooperative
Prey Capture
Territories (small!)
Staking Territories with Chemical
Markers
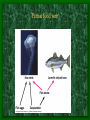
Three-spined
stickleback
courtship behavior
Bee
Communication
Colonial Mammals
Naked Mole Rats
the Common Mole Rat
Kin Selection and Altruism in the
Belding Ground Squirrel
Ecology
• the biosphere
• behavioral biology
• population biology
• community ecology
• ecosystems
Population Ecology
Populations
Life Histories
Population Growth
Population Limiting Factors
Human Population /Growth
Conservation Ecology
Biodiversity Crisis
Conservation at the Population and Species Level
Conservation at the Community, Ecosystem, and
Landscape Levels