* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How can we use this knowledge?
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Ecogovernmentality wikipedia , lookup
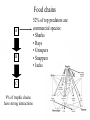
How can we use this knowledge? • We can assign a probability to the next step in the degradation of reefs in particular areas, and take preventive measures to prevent “ecological surprises” plh plc Large herbivores psc Large carnivores psh Small carnivores Small herbivores pab Architectural builders How can we use this knowledge? • We can use the historical trajectories to rank reefs along a gradient of degradation/health and evaluate the efficacy of conservation actions Conclusions 1 • There are general patterns and cause-effect rules • Do not need to monitor every particular case • We can use these general rules to forecast future change and manage accordingly and preventively Food webs: coral reefs Dolphins Caribbean coral reefs - DENSEST SUBWEB Bascompte, Melian & Sala, unpubl. Caribbean coral reefs - SUBWEB Bascompte, Melian & Sala, unpubl. A Food chains with strong interactions are susceptible to strong “cascade” effects B C Food chains A B C 9% of trophic chains have strong interactions 52% of top predators are commercial species: • Sharks • Rays • Groupers • Snappers • Jacks Conclusions 2 • We can take present knowledge on interactions, get the history, and make predictions of the costs and benefits of the removal or increase of particular species • Food web models are good management tools • No MPA anywhere has restored an ecosystem to its mature state • Need to know how mature ecosystems were, and prevent the trap of the illusion of statistical significance Is collapse inevitable? The example of civilizations • Gradual depletion of a resource base, often due to mismanagement • More rapid loss of resources due to environmental fluctuation or climatic shift • Example: the Maya civilization collapsed in the Terminal Classic Period during an extended regional dry period, after reaching great population densities and vast agricultural areas COLLAPSE OF COMPLEX SOCIETIES Intensive exploitation of local resources Increase in human population density Productivity insufficient to support the system Exploitation of peripheric resources (subsidies) Depletion of subsidies/ Further expansion too costly and not profitable No subsidies available Environmental disturbance/ fluctuation COLLAPSE COLLAPSE OF FISHERIES Economic subsidies Intensive exploitation of select species Productivity insufficient (fishery not profitable) Environmental disturbance/ fluctuation Increased capacity No other profitable species available Exploitation of other species Fishing down food webs Marginal return on investment declines dramatically COLLAPSE TRAWLING “ … and [trawling] will not be allowed in any waters except where and when allowed by His Majesty the King by specific authorisation, and only for the period of time specified …” Carlos III, King of Spain, Naples and Sicily 1716 - 1788 Fishing regulations in the Catalan coast, 1752 • Because management actions depend on what managers know at a given time and the models that are available to them, even if a system has exhibited cycles in the past, managers will attribute these cycles to some low probability event What does it take to go forward? + P/B Structure Time (Ecosystem degradation)