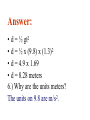* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Motion Dukes oHazzard 08t
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Derivations of the Lorentz transformations wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Speeds and feeds wikipedia , lookup
Variable speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Motion• Chapter 1 pp. 12-29 Speed• a measure of how fast something is moving. • Equation- Speed = distance time You have to MEMORIZE this one! Units for speed• mi/h (mph) • km/h or • m/s Use this to remember the equation! • ( / is read per and means divided by) 1.) What is the speed of a car that has gone 200 km in 4 hrs.? Answer200km 4 hr = 50 km/hr Velocity- describes the speed and direction of something • You can change velocity without changing speed if you turn a corner. • If you travel at 10mph on Lombard street your speed stays the same. 2.) Does velocity change? Answer: Yes, several times Velocity vector• a pictorial representation of velocity • An arrow that shows the direction of travel • Length of the arrow shows the speed of object Vectors can also represent other quantities like force • Shows the direction of the force. • Length of the arrow = magnitude of the force Adding vectors A • Vectors that add together – Component Vectors (arrows A & B) • The sum of component vectors is called a resultant ( arrow C) B Add vectors by lining them up “tip to tail” End up with a parallelogram C • You cannot add velocity vectors with force vectors or acceleration vectors A B Acceleration- the rate of change in velocity • Acceleration = change of velocity time interval Units for Acceleration• km/hr2 Reads kilometers per hour per hour Each hour the speed changes so many kilometers per hour • m/s2 Reads meters per second per second Each second the speed changes so many meters per second • km/h/s Reads kilometers per hour per second Each second the speed changes so many kilometers per hour 3.) A car can go from 0 km/h to 90 km/h in 10 s. What is its acceleration? Answer90 km/h – 0 km/h = 9 km/h/s 10 s These units are the hardest to understand! 4.) What do these units mean? This answer means that each second the car is speeding up 9 km/h Free Fall (Vertical Velocity)• an object falling free of all restraints • v = gt – v- velocity – g- acceleration of gravity » 9.8 m/s2 on earth » during each second of fall the object gains 9.8 m/s in velocity – t- time Calculating Vertical Distance• Freely falling objects only • Equation- d = ½ gt2 – d = distance traveled » Units- meters – g = acceleration due to gravity » Units- m/s2 – t = time of fall » Units- seconds 5.) A person jumps off a cliff and has been falling for 1.3 sec., how far did they fall? Answer: • d = ½ gt2 • d = ½ x (9.8) x (1.3)2 • d = 4.9 x 1.69 • d = 8.28 meters 6.) Why are the units meters? The units on 9.8 are m/s2. Done!!