* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forces
Pioneer anomaly wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Equivalence principle wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
Newton's law of universal gravitation wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
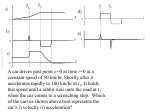
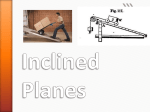
Forces Chapter 4 Forces A push or a pull Gravitational Electromagnetic Weak Strong Sir Isaac Newton Newton’s First Law An object in motion remains in motion and an object at rest remains at rest unless acted on by an outside force. Sometimes called the Law of Inertia Examples Sudden braking Flooring it Seeing stars Inertia A body’s tendency to keep doing what it’s already doing Measured by mass Does not need gravitational force. Newton’s Second Law The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force on the object and inversely proportional to the mass. F ma Units m F ma kg 2 N s Newtons English equivalent is pounds 4.45N=1lb Practice A 2988kg elephant accelerates on a skateboard at a rate of 2.7m/s2. If the elephant is being pushed with a 10,000N force, what is the force of friction? A 58.7N force is applied to a go kart to get it started. If the car starts from rest and accelerates for 4.0s covering a distance of 7.8m, what is the mass of the kart? Newton’s Third Law When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force on the first of equal magnitude and opposite direction Action-reaction pairs Switch the nouns Weight Weight and gravitational force are the same thing. Since acceleration due to gravity (g) is known, we can define weight as: Fg mg In general, we will take care of directional information (positives and negatives) in the problem itself, so we will use +9.8m/s2 instead of -9.8m/s2 Skydiving and Terminal Velocity Practice Problems A skydiver reaches a terminal velocity of 55m/s when in free fall. If the skydiver has a mass of 78kg, how much force is air resistance providing? When starting up the elevator, a rider experiences an acceleration of 1.2m/s2. If the force from the elevator floor is 650N, what is the mass of the rider? Normal Force Force pushing up from a surface When vertical acceleration is zero and the only two vertical forces are gravity and normal force, normal force and gravity are equal. Scales read normal force Elevators Weightlessness (Newton’s Mountain) Friction Depends only on the surfaces, not on velocity Kinetic and static friction Depends on two things, normal force of the object and the combination of surfaces Coefficient of friction, µ equals the ratio of frictional force to normal force. F fr FN Practice A 16.8 kg crate is pushed horizontally along the floor with a force of 207N. If the coefficient of friction is 0.62, what is the acceleration of the crate? A sled is pulled across the snow with a constant velocity. If the sled has a mass of 32.1kg and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.14, what is the magnitude of the pull? A bunch of guys try to push a car out of the mud. They push harder and harder until it becomes unstuck and then push with a constant force. If the coefficient of static friction is 0.54 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.40, what is the acceleration of the car once it starts moving? A crate of chickens is pulled with 145N of force with a rope that is inclined 30° up from the horizontal. If the crate has a mass of 35kg and the coefficient of friction between the floor and the crate is 0.43, what is: The normal force on the crate? The acceleration of the crate, assuming it accelerates horizontally. Tension Upward force coming from a string or rope. All vertical ropes supporting an object account for an equal amount of force unless specified otherwise. Atwood Machine Problems •If mass 1 is 5kg and mass 2 is 7kg, what is the acceleration of the system? m2 m1 Assumptions • a1= a2 • FT1= FT2 Pulley switches which direction is positive. Consider the direction of motion of the box to be the positive direction. Box 1 FT a F ma FT Fg m1a FT m1g m1a Fg Box 2 F ma FT Fg FT m2 a a Fg m2 g FT m2a Putting it together FT m1 g m1a m2 g FT m2 a FT m1 g m1a m2 g m2a FT m1g m1a m2 g m2a m2a m1a m2 g m1g Putting it together cont. m2a m1a m2 g m1g (m2 m1 )a m2 g m1g m2 g m1 g a 1.63 m 2 s m1 m2 Practice Problem m1=8kg m2=4kg Find FT m2 m1 Sign Problems Equilibrium-the state where all forces are balanced and acceleration is zero. Includes both stationary and constant velocity cases. 1st Example If the sign has a mass of 15kg, what is the tension in the string? What is the force the beam exerts on the sign? Assume equilibrium. One component at a time. Set up equilibrium case F F horizontal vertical 0 0 Fy FT sin Fx FT cos Fy FT 23 Fx Fbeam Fg Equilibrium case for vertical F vertical 0 Fy Fg 0 FT sin mg 0 mg FT 376.2 N sin Equilibrium case for horizontal F horizontal 0 Fx FBeam 0 FT cos FBeam 0 FT cos FBeam 376.2 cos 23 346.3N Practice Problem 2 Find the tension in each rope. T1 T2 Break up Components Fy1 F1 sin 1 F1 F2 Fx1 F1 cos1 Fy 2 F2 sin 2 Fx 2 F2 cos 2 Fy1 Fy2 Fx1 Fx2 Fg Horizontal Pieces Since the sign isn’t accelerating horizontally, we can use: Fy1 Fy2 Fx1 Fx2 Fg F x 0 Fx1 Fx 2 0 F1 cos1 F2 cos2 0 F1 cos1 F2 cos2 Vertical Pieces Since the sign isn’t accelerating vertically, we can use: Fy1 F 0 Fy1 Fy 2 Fg 0 Fy2 Fx1 Fx2 Fg F1 sin 1 F2 sin 2 mg 0 Putting the two together F1 cos1 F2 cos2 F1 sin 1 F2 sin 2 mg 0 F2 cos 2 F1 cos 1 F2 cos 2 sin 1 F2 sin 2 mg 0 cos 1 Putting the two together cont. F2 cos 2 sin 1 F2 sin 2 mg cos 1 cos 2 sin 1 sin 2 mg F2 cos 1 F2 mg cos 2 sin 1 sin 2 cos 1 Putting the two together cont. F2 47 9.8 cos 62 cos 34 sin 34 sin 62 383N F2 cos 2 F1 214.6 N cos 1 Ramp Problems Practice Problems A box slides down a frictionless ramp. If the box has a mass of 12kg and the ramp is inclined at an angle of 32 degrees, what is the acceleration of the box? A 76kg box slides down a ramp inclined at 21 degrees. If the acceleration of the box is 1.2m/s2, what is the coefficient of friction between the box and the ramp? Random Practice Problems A 28kg box is pulled at an angle of 18o up from the horizontal with a force of 145N. If the coefficient of friction between the floor and the box is .32, what is the acceleration of the box? A dead pig has a µk of .21 and a µs of .43 when sitting on a book cover, how far will the book cover need to be tilted to start the pig carcass moving? Once it starts moving, how quickly will it accelerate? m1=13kg m2=9kg μk=.11 What is a?