* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Beyond Europe-1213-wk6 T ed
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
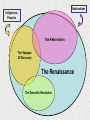
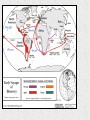
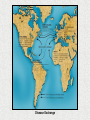
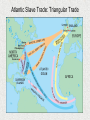
History of the Ancient and Medieval World Beyond Europe Walsingham Academy Ms. Hockaday Starter- Read “Witness History” on page 472 • Respond to the following question: – How did a small number of Spanish conquistadors conquer huge Native American empires? Nationalism Indigenous Peoples The Reformation The Voyages Of Discovery The Renaissance The Scientific Revolution Whose viewpoint? More Views Conquest in the Americas • Columbus meets the Taínos – Relationship went from good to bad…why? • Taínos didn’t pay homage to Christian symbols • Columbus claimed land for Spain & took prisoners • Conquistadors defeat Native Americans despite being outnumbered – How? • • • • Guns & cannons Armor Horses Diseases (no immunity) Cortés Conquers Mexico • From Cuba; traveled to Tenochtitlan (Aztec) • Through alliances w/others, Cortés was able to fight and conquer the Aztecs • The emperor, Moctezuma, was willing to work with Cortés • Cortés tricked him into signing over his land & treasures Pizzaro Takes Peru • Pizzaro was interested in the Incas in Peru • After a civil war in Peru, Pizzaro captured the ruler & killed him • Using their advantages (which were…?) they overran the Incans and added to the Spanish empire (Ecuador and Chile) Effects of Spanish Conquistadors • Spain becomes a superpower • NA lost faith in their gods and converted to Christianity • Most of the world is now connected by sea routes – Cultural diffusion History Mind-Mapping: 5 W’s and an H (use handouts & pp. 472-476) • For each of the First Conquests in the Americas, answer the following questions: – WHO: – WHAT: (ex—things were going well until Taínos mistakenly did not recognize Christian symbols) – WHEN: – WHERE: – WHY: – HOW: (ex—disease) Tonight’s Homework • A CHANGE–READ Pages 477-481 and complete the Venn diagram on page 480 Starter: Read “Traveler’s Tales” on pp. 474-475 • Reply to the Thinking Critically Questions • Be prepared to share your responses Spain and Portugal Treaty of Tordesillas, 1494 In-Class Activity 1. View The Last Conquistador Video Clip and answer questions 2. What were motivating factors of Portuguese and Spanish ventures beyond Europe? 3. Compare and contrast the patterns of Portuguese and Spanish ventures beyond Europe? 4. Identify technological advances which made possible the voyages of exploration during this period. 5. Name the cultural traditions that came together to shape life in the New World. How did the colonial social order reflect the interactions of these traditions? Trade & The Struggle for North America • Starter—Read the Biography on Jacques Cartier (page 483) answer the following question: – Why were Cartier’s discoveries undervalued at the time? Building New France • Jacques Cartier claimed much of Canada or New France for the French • Jesuits followed…why? • First settlement: 1608 with Champlain’s colony in Quebec • Farming was not pleasurable due to Canada’s climate; turned to fishing (cod), fur trapping & trading The 13 English Colonies • John Cabot: 1497; from Venetian discovered fishing grounds off the coast of Newfoundland & claimed the area for England • 1st successful permanent colony was in 1607: Jamestown – Meant to bring wealth & prosperity; many died – Few survived with help from Native Americans – Growth of tobacco The 13 English Colonies • Plymouth, Massachusetts- Pilgrims in 1620 (Protestants who rejected the Anglican Church) • Signed the Mayflower Compact • Survived with help from Native Americans The 13 English Colonies New England • Fishing • Timber • Shipbuilding • Massachusetts set up for those who were persecuted • Connecticut & Rhode Island were started from dissenters of the Massachusetts colony • NH was a proprietary colony Middle Colonies (Mid Atlantic) • Grain • Some small farm ventures • Shipbuilding & lumber also • Pennsylvania began for those who were persecuted • NY. NJ & Delawarecommercial ventures Southern • Plantations • Cash crops—tobacco and rice • Virginia was a commercial venture • Maryland was started by a Lord (Baltimore) who wanted freedom from Catholic Church • Carolinas-commercial venture • Georgia was a prison colony for debtors Struggling For Power FrenchPresent Day Canada & Central US SpainPresent Day Texas and Florida English & Dutch- East Coast Native Americans also want in on the battle English colonies experienced selfgovernment & when that was taken away, issues began… French and Indian War (1763) Treaty of Paris gave England control of North America Columbian Exchange • Started with Columbus—hence the name Disease Exchange Changes In Europe 1. What was one change caused by European exploration? – Prices rose (inflation) – Capitalism (investing money to make a profit) – Mercantilism (export more than you import) 2. Imagine that you live in Europe in the 1600s. What is one way that the Columbian exchange might affect you? – Exposure to new goods – Nobility less powerful; peasant: no change Atlantic Slave Trade: Triangular Trade Atlantic Slave Trade/ Middle Passage 1. What were two effects of the slave trade? – Many Africans died on trip to new world – Some societies and small states disappeared – New states that depended on slave trade developed – Conflicts arose in Southern Africa 2. When did the slave trade officially end in the British empire? – 1833 TULIPMANIA A tulip, known as "the Viceroy", displayed in a 1637 Dutch catalog. Its bulb cost between 3000 and 4200 florins depending on size. A skilled craftsman at the time earned about 300 florins a year was a period in the Dutch Golden Age during which contract prices for bulbs of the recently introduced tulip reached extraordinarily high levels and then suddenly collapsed. At the peak of tulip mania in February 1637, some single tulip bulbs sold for more than 10 times the annual income of a skilled craftsman. It is generally considered the first recorded speculative bubble (or economic bubble), The term "tulip mania" is now often used metaphorically to refer to any large economic bubble (when asset prices deviate from intrinsic values). Assignment 1: In-Class Activity Assignment 1: due Wed. 5/1 • Study slides 2-4 and anticipate the questions. • Read photocopies: – The Search for Spices – Conquest in the Americas – Spanish and Portuguese Colonies • Using complete sentences, answer 6 Review Questions • Follow link and read. Astrolabe: Paris Observatory (A School Project: Made by 16-year-old) Assignment 2: due Wed., 5/1 1. Read text, pp. 477-481 2. Complete Graphic Organizers: Spanish Colonies in America, Empires in the Americas. A Missionary Protests How does the painting of the mine (pp. 477) at Potosí reinforce Las Casas’s view? Assignment 3: due Thurs. 5/2 •Read photocopies: Turbulent Centuries in Africa Struggle for North America Changes in Europe •Using complete sentences, answer 6 Review Questions Native village (North Carolina) as seen by artist John White of Sir Walter Raleigh’s expedition, 1585 Assignment 4: due Fri. 5/3 1. Read text, pp. 491-497 2. Define mercantilism, capitalism. 3. Complete Graphic Organizers: Recognize Sequence. 4. Explain how Tulipmania reflected the economic changes of its time. Uniting the World How do the visuals reinforce the idea that Smith expresses? Question 1 Why were Portugal and Spain the leaders in European exploration? Question 2 How did the Portuguese and the Spanish differ in their approaches to exploiting new lands? Question 3 1 2