* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Greek Achievements
Ancient Greek warfare wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek temple wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Greek mythology wikipedia , lookup
Greek contributions to Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Acropolis of Athens wikipedia , lookup
Classical order wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek medicine wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek religion wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek architecture wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
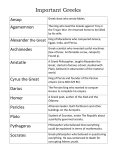
Greek Achievements Chapter 9: Section 4 Art, Philosophy, & Science Debra Fisher-Nichols Elmore Park Middle School Statues and Paintings People were portrayed in their ideal form, paying close attention to details. Marble and stone were realistically carved, showing muscle and details of the fabric, many Greek statues look as though they could come to life at any moment. Painting on pottery was usually only done in two colors (red and black) Architecture Greek architecture had three styles: Doric, Ionic, Corinthian. Each of these styles is clear when you look at the building’s columns. Doric (simple) Ionic (scrolls) Corinthian (acanthus leaves) Temples Were designed using columns on the exterior The Parthenon is the most impressive of temples that is still standing. The exterior and interior were decorated with carvings. Phidias, considered the greatest sculptor in all of Greece, created a magnificent statue of Athena on the inside of the Parthenon. Greeks created new forms of writing including: DRAMA (plays about tragedies and comedies) HISTORY-written accounts of actual events DRAMA: Tragedies and Comedies Drama (plays) was part of religious ceremonies. Scenes were performed by actors and singers to honor the gods. Attending these plays became one of the most popular form of entertainment, especially in Athens. One form of Drama was the Tragedy. Tragedies described hardships faced by Greek heroes Famous writers of tragedies Aeschylus –considered the father of tragic drama Sophocles-wrote the famous play “Oedipus the King,” (429 BC) about a man who unknowingly kills his father. Euripides-wrote “Heracles” first performed in 416 BC Another form of Drama is the Comedy: Comedies made fun of people and ideas Aristophanes - used comedy to make serious points about war, courts of law, and famous people History Herodontus-considered the father of history, however, his accounts were mostly second hand and included references to gods and goddesses. Thucydides-An Athenian and the father of “scientific history” because of his strict standards of evidence gathering without reference to the intervention by the gods. He wrote about the Peloponnesian War. He tried to keep his account unbiased or neutral. Philosophy A group of people who began to question the explanations about life that Greek mythology gave Believed in the power of the human mind to think, explain, and understand life. Socrates Considered the greatest philosopher Socratic method - would teach by presenting a question and then challenging the answer He encouraged students to question their own beliefs This made leaders angry and he was tried and found guilty of corrupting the youth His friends and students watched as Socrates was given hemlock, a poison, drank it, and died Plato Was a student of Socrates Started a school - The Academy, where students, philosophers and scientists could come to discuss ideas. His most famous writing was The Republic The Republic talked about Plato’s idea for an ideal society based on justice and fairness, and run by philosophers Aristotle A student of Plato Believed everything should be done in moderation (in balance-not too greedy nor too giving) Believed moderation was based on reason (clear and ordered thinking) Made great advances in logic. He argued that you could use facts to figure out new facts. Aristotle inspired Greek scientists to look closely at the world we live in. Mathematics Euclid - was a mathematician who taught in Alexandria, Egypt who focused on geometry Many of the geometry rules you study in math comes from him Pythagoras-made influential contributions to philosophy and mathematics. The Pythagorean theorem (the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides) is named for him. SCIENCE Thales -Many consider him the first Greek philosopher of science because he paved the way to the scientific method. Thales attempted to explain natural phenomena without reference to mythology and was tremendously influential in this respect. Thales of Miletus 624 BC – 546 BC Medicine Doctors studied the human body to understand how it worked. Hippocrates - wanted to find ways to cure disease. Best known for the Hippocratic Oath how doctors should behave. Engineering Made discoveries that we still use today. (especially the methods in which we build large structures) Archimedes - a scientist who invented the water screw still used by farmers to bring water from a lower level to a higher one to water crops. Some inventors even came up with mechanical toys. Other achievements to know Lyceum- a gymnasium and before that a public meeting place in a grove of trees in Classical Athens. The Royal Library of Alexandria, or Ancient Library of Alexandria, in Alexandria Egypt-one of the largest and most significant libraries of the ancient world. It was dedicated to the Muses, the nine goddesses of the arts. Acropolis-the location of The Parthenon and other temples in ancient Greece Temple of Apollo-an ancient temple in Delphi built in the 6th century BC Review What were the two main types of art? (Describe) What were the three styles of architecture? Who were the three main philosophers? Who were Euclid and Pythagora? What discoveries were made in engineering?