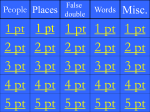
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Legacy of Classical Greece
Cappadocian Greeks wikipedia , lookup
Classical order wikipedia , lookup
Acropolis of Athens wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek warfare wikipedia , lookup
Pontic Greeks wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Regions of ancient Greece wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of Greece and the Greek world wikipedia , lookup
Greek contributions to Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek cuisine wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek architecture wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek medicine wikipedia , lookup
Greek Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
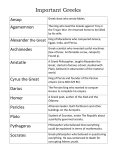
The Legacy of Classical Greece In this lesson, students will be able to identify accomplishments of classical Greek civilization. Students will be able to identify and/or define the following terms: Democracy Parthenon Socrates Pythagoras E. Napp A classical civilization is a civilization that has given the world important ideas and inventions that people still use today. E. Napp Ancient Greek civilization is considered a classical civilization. E. Napp Athenian Democracy • The ancient Greek city-state of Athens developed the first democratic government. • A democracy is a system of government where citizens participate in government. • Only free men born in Athens could be citizens. Women, slaves, and foreigners could not vote. E. Napp The ancient Athenians were the first people to use voting as a form of participation in government. E. Napp Architecture • The Greeks built temples with beautiful columns. • Greek architecture still influences people today. • Many government buildings in the United States are modeled after Greek temples. E. Napp The Parthenon was a Greek temple to the goddess, Athena. Notice the use of columns. E. Napp The U.S. Supreme Court building is clearly influenced by the Parthenon. E. Napp Classical Greek Philosophy • The ancient Greeks were the first students of philosophy. They wanted to know the meaning of life and how people should live. • Greek philosophers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle still influence people today. • Socrates encouraged people to think for themselves and to ask questions. E. Napp Socrates was a great Greek philosopher. He was tried and found guilty of corrupting the youth of Athens. For encouraging people to ask questions, he was forced to commit suicide. E. Napp The Greek Mathematicians • The ancient Greeks also made advances in mathematics. • Pythagoras, Euclid, and Archimedes were important Greek mathematicians. • The Pythagorean theorem examines the relationship between the three sides of a right triangle. E. Napp The ancient Greeks gave us many important mathematical theorems. E. Napp The Legacy of Classical Greece • A legacy is defined as something handed down from the past. • The ancient Greeks have passed down many important ideas and inventions to our modern world. • Democracy, the use of columns, mathematical ideas, and philosophies are just a few of the ideas passed down to modern people from the ancient Greeks.. E. Napp The ancient Greeks were the first people to perform plays and write comedies and dramas. E. Napp Questions for Reflection: • Define legacy. • List two important contributions of the ancient Greeks to the modern world. • How do Greek ideas concerning government still influence us today? • How do Greek ideas concerning architecture still influence us today? • Why is ancient Greece considered a classical civilization? E. Napp