* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Greeces last stand of 300
Pontic Greeks wikipedia , lookup
Greek contributions to Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of Greece and the Greek world wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek religion wikipedia , lookup
Peloponnesian War wikipedia , lookup
Greek Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Spartan army wikipedia , lookup
Ionian Revolt wikipedia , lookup
First Peloponnesian War wikipedia , lookup
Corinthian War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Eurymedon wikipedia , lookup
NO BELLWORK TODAY!
• Spend the first part of class meeting with
your group and reviewing your Greek
Civilization Graffiti Board.
• Discuss the following….Who is talking
about what? How will you explain things to
the class? What are the most important
points? Everyone must contribute!
• Be ready to present shortly!
Greek Civilization
• Greeks are most known for their contribution to modern society.
• Including classical art, architecture, drama, philosophy, history,
science, and the Olympic games.
Visual Arts
Greek Drama
The Olympics
Philosophers
Socrates
Plato
Aristotle
Historians
Science
REVIEW
1. What were the themes of Greek society? How were
those incorporated into Greek culture?
2. Explain the advances made in Greek drama.
3. How did Greek philosophers change the way people
thought?
4. How did Greek history impact Modern America?
5. Why did Sparta and Athens distrust each other?
Conflict in Ancient Greece
Persian Wars
Peloponnesian War
Review
• Why were Greece and Persia
enemies?
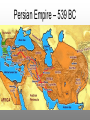
Persian Empire – 539 BC
The Persian Wars
• In 490 BC, Persian forces (led by Darius I) landed near
Athens.
• The outnumbered Greeks staged a surprise attack and
defeated the Persians!
• In 480B.C., the Persians returned to Greece (now led by
Xerxes I)
• 7,000 Greeks (Spartans/Athenians) vs. 100,000 Persians
• Greek navy destroyed the entire Persian fleet.
• The Persians responded with a sneak attack on the
remaining 300 Spartan warriors – Battle of Thermopylae
Persian Wars – Battle of Thermopylae
• Thermopylae ("hot gates") was a
pass the Greeks tried to defend
• Spartan King Leonidas was in
charge of the Greek forces. He
had three goals:
– Restrain & delay the strong Persian
Army
– Keep them from attacking the Greek
navy (under Athenian control Themistocles)
– Block them long enough so they
would be forced to sail back for food,
water & supplies
The Last Stand of the 300
• For the rest of class,
you will be watching a
video on the last stand
of the 300 at the Battle
of Thermopylae.
• Answer the questions
on the worksheet
• Pay attention! This
information will be
included on the unit
test
BELLWORK (Block 2)
1. Explain the role of the following men in the Persian Wars:
Darius I, Xerxes I, Leonidas & Themistocles.
2. Why did Sparta and Athens (traditional enemies) decide to
fight together in the Persian Wars?
3. How did the geography of Thermopylae help the Greek
army?
4. Describe the military training of Spartan boys.
5. THINKER: Why would Leonidas, already expecting defeat at
Thermopylae, send his army away but keep his strongest
300 soldiers to fight?
Persian Wars – Battle of Thermopylae
• A Persian-sympathizer & traitor named Ephialtes led the
Persians around the pass showing them where to attack from
behind.
• Expecting defeat, Leonidas sent away most of his troops.
• The remaining 300 Spartan warriors fought the Persians &
blocked the pass long enough so the rest of the Greek army
could escape.
• All 300 warriors were killed - Greece accepted defeat
• After their victory, the Persians marched to Athens and burned
it to the ground (already been evacuated)
• The Greeks would defeat Persia and re-capture Athens a year
later, in 479 B.C.
The Peloponnesian War
• War between Sparta and Athens that lasted
from 431BC to 404BC.
• Sparta allied with the Persians
• A plague struck Athens and killed 1/3 of their
population
• Persian-financed Spartan navy destroyed
Athens fleet.
• Athenians surrendered