* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cell theory
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
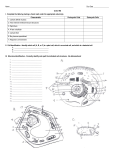
• All living things are made of cells, the smallest unit that can carry on all the processes of life • In 1665, Robert Hooke observed the first cells from thin slices of cork. He gave them the name "cells" because they reminded him of small rooms or cells that monks lived in. • In 1675, Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first person to observe living cells. He looked at protozoans from pond water. CELL THEORY • About 150 years later scientists organized their observations into a cell theory: • - All living things are composed of one or more cells. • - Cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism. • - Cells come only from existing cells. Prokaryotic Cells (Bacteria) • The average size is about 1 micrometer. Bacteria have no nucleus and no membrane-bound organelles. An organelle is a cell component that performs specific functions for the cell. Cell Membrane • separates the cell from its environment. • It regulates what moves into and out of the cell. • The Fluid Mosaic Model: the cell membrane is made up of 2 layers of phospholipids with proteins embedded throughout. These lipids and proteins constantly move laterally creating a fluid motion. Cytoplasm • the entire contents of the cell, except the DNA. Ribosomes • site where proteins are made. Nucleoid • tangled ball of DNA; tells cell what proteins to make. • It is not called a nucleus because the DNA is not contained within a membrane. Plasmids • small rings of DNA (separate from the nucleoid). Pili (pilus) • appendages that allow the bacteria to adhere to other surfaces. Flagella • long extensions that aid in movement Cell Wall • outer rigid layer; maintains the shape of the cell and adds protection.