* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Virus Notes (18.2)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
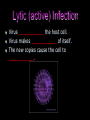
Viruses (18.2) State Standard SB3D. Compare & contrast viruses with living organisms. Viruses—An Exception A virus is a nucleic acid (__________) surrounded by a protein coat (__________). Why aren’t they considered to be living? Viruses are _______________, nor are they made of cells. Viruses __________________ without a __________ cell. Viruses __________ the machinery needed to carry out the functions of life. Because viruses are __________, they usually are not placed in the biological classification system. More virus traits… the core can be made of _____ or _____ (but never both!) very __________ NOT __________ Can reproduce by __________ living cells. The capsid helps the virus __________ to the host cell. E. Coli and the Bacteriophage What it looks like in real life There are two types of viral infection cycles: • __________ (Active) • __________ (Dormant) Lytic (active) Infection Virus __________ the host cell. Virus makes __________ of itself. The new copies cause the cell to __________. The Lytic Cycle Lysogenic (dormant) Infection A virus __________ its DNA into the DNA of the host cell. The virus’s __________ is __________ (copied) along with the host cell’s DNA. The cell does NOT __________ immediately. Certain conditions can cause the __________ virus to __________ to an active lytic cycle. The Lysogenic Cycle Viruses often cause observable __________ Antibiotics are __________ against viruses, because viruses are not __________ Ex. AIDS, Smallpox, Polio, Measles, the Common Cold Vaccines Since viruses can’t be cured, our only defense against them is __________ We accomplish this through the use of __________ Vaccines contain a __________ or __________ form of the virus that is __________ into the body. Retrovirus Changes DNA into __________ Mutates quickly And example of a Retrovirus is __________