* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
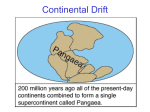
The Layers of the Earth The Layers of the Earth The Earth is composed of four different layers: • The crust, mantle, outer core and inner core. layers of earth The Crust • Earth’s thinnest layer • Made up of silicon, oxygen and magnesium The Crust The crust is composed of two different rock types: -Continental crust: thicker, less dense, older, made of granite -Oceanic crust: thinner, more dense, younger and made of basalt Tectonic Plates • The crust is broken up into “plates” that move around on top of the mantle The Mantle • • • • The thickest layer of the Earth. Made up of silicon, magnesium and iron Lithosphere: the crust and top of the mantle Asthenosphere: below the lithosphere, the upper mantle –Made up of plastic-like rock that flows and causes plates to move • is the mantle liquid? (start at 3:24) The Mantle • Mesosphere: the lower part of the mantle • Makes up most of the mantle and is molten rock Earth’s Layers • Sci Show Earth's not so juicy center The Outer Core • Made up of liquid nickel and iron • Convection currents in the outer core create the Earth’s magnetic field The Inner Core • Made of solid iron • Remains in a solid state because it is under extreme pressure Inner Core • The Earth’s core is so hot because the: • heat of formation and • radioactive decay Why is the core so hot? Heat of Formation • Heat of formation: the formation of earth created intense heat. • Some of that heat is still inside Earth’s core • Accounts for 50% of earth’s internal heat Radioactive Decay • Radioactive Decay: as radioactive elements in rocks decay they give off energy in the form of heat (ex. uranium and thorium) • Accounts for 50% of earth’s internal heat Layer Lithosphere Asthenosphere Mesosphere Outer Core Inner Core Thickness 5-60 miles 430 miles 1800 miles 1400 miles 760 miles Made out of Rock: Granite and Basalt Rock: Silicate materials Rock: Silicate materials Metal: iron and nickel Metal: Iron State of matter Solid Plastic-like Molten (liquid) Molten (liquid) Solid Unique • Thinnest layer • 2 types Lithospheric plates move on top of this layer Convection currents cause the plates to move Creates Earth’s magnetic field Under the highest pressure Properties Kola Superdeep Borehole: Russia • Deepest hole ever dug: scientific expedition • 12,262 meters (7.6 miles) • The temperature at this depth was 180°C (356°F), at which point the rock became more like a plastic than a solid, stopping further drilling • how deep have we drilled? Argyle Diamond Mine: Australia • Largest hand dug hole in the world • Largest volume of diamonds produced – 600 meters (1,970 ft) Chuquicamata: Chile Udachnaya: Russia Mirny Diamond Mine: Russia Bingham Canyon Mine: Utah Sinkhole: Guatemala Great Blue Hole: Belize Darvaza:Turkmenistan • The door to hell How do we know all of this? • Scientists use seismic waves to analyze Earth’s layers • Shadow zones: places on earth where no seismic waves reach • S-wave: a type of earthquake wave that cannot travel through the liquid outer core Mantle Convection • Convection: the transfer of heat through the movement of a fluid • Hot magma rises and cooler magma sinks • The rising and sinking magma creates a convection current • Convection currents cause tectonic plates to move