* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Benchmark SC.F.1.2.4: The student knows that similar cells
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
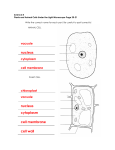
Benchmark SC.F.1.2.4: The student knows that similar cells form different kinds of structures Ophir Ortiz GLE’s Covered in this Presentation • Fourth 1. knows that living things are composed of cells. 2. knows that processes needed for life are carried out by the cells. • Fifth 1. uses magnifying tools to identify similar cells and different kinds of structures. 2. knows the parts of plants and animal cells. 3. understands how similar cells are organized to form structures (for example, tissue, organs) in plants and animals. Outline • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • What is a cell? “How Big” Applet 1 Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells Parts of Bacteria Cells Hands-On Activity 1/ Worksheet 1 Parts of Plant Cells (hyperlinked) Parts of Animal Cells (hyperlinked) Parts of a Cell Applet 2/ Worksheet 2 Brain Pop Video 1: Cell Structure Hands-On Activity 2: Build Model of Animal Cell and Plant Cell using Play-doh and Candy/Pasta Brain Pop Video 2: Cell Specialization Nutrient Transport into Cells Hands-On Activity 3/ Worksheet 3: Nutrient Transport into Cell Membrane Tissues- Animal (human) and Plant Organs- Human Organs Game Applet 3 • Appendix- Play-doh recipe, Additional Resources/Links Cell Overview • All living organisms are made up of cells • “building blocks of life” • Mold on bread, your dog, pine trees, etc. are all made up of cells • Cells are so small, they need to be magnified to be seen • Microscopes are used to magnify cells Cell Overview There are more than 10 trillion cells, and over 200 types of cells in the human body, that very greatly in size, shape, and function!!! How Big are Cells? Why are cells important? • Cells can: – – – – take in nutrients, convert these nutrients into energy carry out specialized functions reproduce as necessary • Each cell stores its own set of instructions (DNA) for carrying out each of these activities • Depending on the type of cell, DNA may be stored inside the nucleus, or it is free floating inside the cell CELL NUCLEUS The Command Center The cell nucleus acts like the “command center” of the cell It consists of a nuclear envelope, (the outer membrane) and nucleoplasm It regulates all cell activity In the nucleoplasm you can see chromatin and the nucleolus http://biology.about.com/gi/dynamic/offsite.htm?site=http://personal.tmlp.com/Jimr57/textbook/chapter3/chapter3.htm Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic • There are two general classes of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic Cells: found in one-celled organisms; do not have a nucleus (bacteria) Eukaryotic Cells: found in organisms composed of many cells; cells have a membrane-bound nucleus (plant cells, animal cells) Prokaryotic: Bacteria Cell Parts of Bacteria Cells Cell Part Function cell wall maintain shape capsule protection flagella long “arms”, for movement where DNA is located nucleoid pili plasma membrane these help cells attach to each other cell covering that allows certain nutrients into or out of the cell What is bacteria? • Bacteria are one-celled organisms that reproduce very quickly • Some are good, some are bad! • Good bacteria are in your stomach, in yogurt, and in bread. Yum! Leptospira, which causes serious disease in livestock Hands-on Activity 1/ Worksheet 1 “Caught Dirty-Handed” Reference: http://www.microbe.org/experiment/dirty-handed.asp Eukaryotic: Animal Cell Parts of Animal Cells Cell Part Function cell membrane covering that controls nutrients into or out of the cell centriole important in cell division process centrosome important in cell division process cytoskeleton a “skeleton” inside the cell cytosol the “soup” inside cells endoplasmic reticulum makes “proteins” (we need proteins to live, like those found in meat and nuts) golgi “packages” molecules for transport Parts of Animal Cells (cont’d) Cell Part Function lysosome kills bacteria mitochondrion makes energy for the cell to function inside the nucleus nucleolus nucleus peroxisome secretory vesicle vacuole control center of the cell, contains DNA for protection “packages” certain chemicals helps in getting rid of waste products Eukaryotic: Plant Cell Parts of Plant Cells Cell Part Function cell membrane covering that controls nutrients into or out of the cell cell wall protective barrier centrosome chloroplast important in cell division process contains chlorophyll cytoskeleton helps maintain shapte cytosol “soup” inside the cell endoplasmic reticulum makes “proteins” Parts of Plant Cells Cell Part Function golgi “packages” molecules for transport lysosome kills bacteria mitochondrion makes energy for the cell to function nucleus nucleolus control center of the cell, contains DNA inside the nucleus peroxisome for protection vacuole helps in getting rid of waste products Parts of a Cell Applet Brain Pop Video 1: Cell Structures Hands-on Activity 2: Build Animal and Plant Cell Models using Play-doh and Candy/Pasta In this exercise, the student will become familiar with the different parts of the animal cell and the plant cell. This will be accomplished by using playdoh as the “cytoplasm”, seran wrap as the “cell membrane”, and various candies and pasta for other components of the cells. Reference: http://www.edu.pe.ca/gray/class_pages/rcfleming/cells/demos.htm Finished Model of Animal Cell Cell Membrane Vacuole Secretory Vesicle Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus Golgi Apparatus Cytoplasm Vacuole Animal Cell Finished Model of Plant Cell Cell Membrane Nucleolus (Seran wrap) ER Nucleus Lysosome Chloroplast Cytoplasm Peroxisome Vacuole Golgi Apparatus Cell Wall (Al. foil) Plant Cell Mitochondrion Brain Pop Video 2: Cell Specialization How do Nutrients Enter Cells? • Just like we need food to get energy, cells also need food (nutrients) • All cells have a thin cover called the cell membrane • Nutrients must pass through this cover (membrane) in order to get inside the cell – One way in which nutrients enter the cell is called “Diffusion” Hands-on Activity 3/ Worksheet 3: Nutrients through the Cell Membrane (Diffusion) • Objective: - This shows how nutrients (iodine) pass, or diffuse, through the cell membrane (plastic bag) • Materials: – Beaker – Iodine – Cornstarch – Sealable plastic sandwich bags • Procedure: Step 1: Place 2 tsp. cornstarch in bag Step 2: Squeeze out as much air as possible, then seal bag. Step 3: Pour 1c. (~240mL) water into beaker Step 4: Add 20 drops of iodine into beaker with water Step 5: Place bag inside beaker, making sure all of cornstarch comes into contact with iodine/water mixture Step 6: Wait 25 min; most of the cornstarch will turn purple What Happens When a Number of Cells Get Together??? • The simplest living creatures are composed of simple cells, but in complex organisms such as human beings and plants, the hierarchy continues on to the tissue level • Tissues are groups of similar cells that have a common function Human Tissues Tissue Type Description Where it is found in the body Epithelium Cover organ surfaces Skin, digestive tract Connective Holds everything together Blood, bone, cartilate Muscle Has filaments that contract Muscles Nervous Main component of Brain, spinal cord nervous system Human Tissues Epithelium Connective cartilage Muscle cardiac Nervous central nervous system Plant Tissues Type of Tissue Description Where it is found in plant Meristematic Division of new cells for Inside plant body new growth or repair Epidermis Cells forming the outer Cover leaves, plant surface body Vascular Transport fluids and nutrients Ground Manufactures nutrients Center of plant body by photosynthesis Inside plant body Plant Tissues Organs • An organ is a structure composed of at least two tissue types • Examples of organs in humans include kidneys, spleen, liver, heart, lungs Appendix Recipe for Play-doh • • • • • 2 1/2 cups of flour 1/2 cup salt 2 packages dry unsweetened Kool-Aid 2 cups boiling water 3 tablespoons oil Recipe obtained from: http://k2.kirtland.cc.mi.us/~balbachl/kidrecip.htm#Doh Additional Resources/ Links • Bacteria hands-on activity: How Do You Make Perfect Yogurt? http://www.uen.org/Lessonplan/preview.cgi?LPid=2515 • Experiments dealing with bacteria/germs http://www.microbe.org/experiment/experiments.asp • “Cells Alive” interactive website http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/plntcell.htm • Link to Free BrainPop Short Videos, various topics http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0078617022/student_view0/brainpop_movies.html Additional Resources/ Links • Various science- related applets http://www.iknowthat.com/com/L3?Area=Science+Lab& COOK • Animal Cell Coloring - general animal cell, coloring http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/cellcolor.html • Plant Cell Coloring - plant cell http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/cellcolor-plant.html • Cell Theory Rap - poem to help learn about cells http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/cellrap.html Additional Resources/ Links Cell City Analogy - worksheet that describes a city, comparing to organelles http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/cell-analogy.html Organs Game (from Slide ) and other virtual games dealing with the human body http://www.bbc.co.uk/science/humanbody/body/index_interactivebody.shtml Animal Tissue slides http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/BioBookAnimalTS. html Plant tissue http://www2.mcdaniel.edu/Biology/botf99/tissimages/tiss1.html Questions???