* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10.4_Cell_Differentiation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
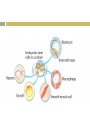
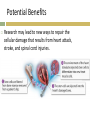
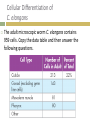
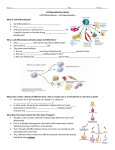
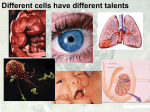
1 Review What happens during differentiation 2 Review What are stem cells Compare and Contrast How are embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells alike and how are they different 3 Form an Opinion How might technological advances help address the ethical concerns surrounding stem cell research CH 10 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION 10.4 Cell Differentiation All organisms start life as just one cell Embryo Early stage of development most multicellular organisms pass through Cells become more differentiated and specialized. Differentiation Process of cells becoming specialized. Cell’s role can be determined at a specific point in development. Differentiation in Mammals Controlled by a number of interacting factors in the embryo Chemical signals Regulatory factors Interaction between cells Adult cells generally can no longer differentiate. Stem Cells Unspecialized cells from which differentiated cells develop Totipotent Can form all the tissues of the body Only the fertilized egg and first few divisions Embryonic Stem Cells Pluripotent Capable of developing into many, but not all, cell types Located in inner mass of cells of blastocyst Blastocyst Early embryo stage with a hollow ball of cells with a cluster of cells inside Adult Stem Cells Multipotent Can produce many types of differentiated cells Typically produce only the types of cells that are unique to that tissue where they are located. Potential Benefits Research may lead to new ways to repair the cellular damage that results from heart attack, stroke, and spinal cord injuries. Ethical Issues Most techniques for harvesting, or gathering, embryonic stem cells cause destruction of the embryo Government funding vs. private funding. Cellular Differentiation of C. elangans The adult microscopic worm C. elangans contains 959 cells. Copy the data table and then answer the following questions. 1. 2. 3. Calculate Calculate the percentage of the total cell number reprented by each tissue or organ listed including ‘other’. Infer Why does C. elanans make an ideal model for studying cellular differentiation Infer Why would it be more difficult to map the differentiation patterns in a different organisms like a mammal