* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation 2
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Armillary sphere wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Celestial spheres wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
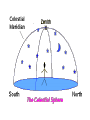
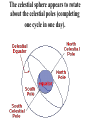
Keep Looking Up Topic 2 Part 1 ``Astronomy compels the soul to look upward and leads us from this world to another.'' - Plato Early Astronomy Early Models Big Dipper Orion Scorpio Winter sky The celestial sphere appears to rotate about the celestial poles (completing one cycle in one day). • Celestial north pole stays still (North star aka Polaris) • Stars appear to move in counterclockwise fashion. Question: What causes the observed circular motions of the stars, Sun, Moon, and planets about the celestial pole? • Hypothesis 1: The Earth is stationary, and the stars, Sun, Moon, and planets revolve around it. • Hypothesis 2: The stars, Sun, Moon, and planets are not revolving about the Earth; it is the Earth which is rotating about its polar axis, once per day. This or that? The Sun moves west to east relative to the stars (completing one cycle in one year). Question: What causes this apparent motion of the Sun relative to the background stars? • Hypothesis 1: The Earth is stationary, and the Sun revolves around it at a slightly slower rate than the celestial sphere does. • Hypothesis 2: The Earth revolves around the Sun, once per year. This or that? The Moon moves west to east relative to the stars (completing one cycle in one month). Question: What causes this apparent motion of the Moon relative to the background stars? • Hypothesis 1: The Earth is stationary at the center of the universe, and the Moon revolves around it a a slower rate than the celestial sphere does. • Hypothesis 2: The Moon revolves around the rotating Earth, once per month. The planets sometimes move west to east, sometimes east to west, relative to the stars. Wanderers • Only 5 planets to the naked eye. • Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn This or that?