* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Center for Origins Studies: CalSpace
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
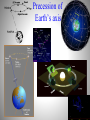
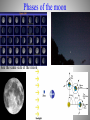
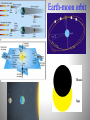
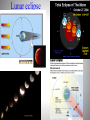
Daily motion of the sky Spin of the Earth Poles and equators Sun’s path at different latitudes Constellations: patterns in the sky Celestial sphere Horizon Southern sky Summer Seasonal appearance winter Sun’s path in the sky Seasonal position of the Sun Earth’s orbit around the Sun Precession of Earth’s axis Phases of the moon See the same side of the moon The moon and the Earth Earthshine Geometry solar eclipses Earth-moon orbit Lunar eclipse Daily motion of stars Deductions: 1) Earth spins 2) Spherical shape 3) Moon reflects Sun’s light 4) A coordinate system for the sky Planets as Physical Bodies Rather than Gods Diameter D D Diameter Hypothesis: Sun is hot piece of stone. How big? How far away? Anaxagoras (500-428 BC) First day of summer (June 21) at noon when Sun Is Pay a soldier to pace off: s = 800 km. r highest in the r/s = 8d/d = 8 r = 8s = 6400 km; Sky. D/r = 0.5o = 0.5o( rad/180o) = 0.009 D= 58 km Syene Alexandria s 8d d Anaxagoras concludes that Sun is a flaming rock smaller than Greece. Wrong! But more important is idea that Sun is a physical body, not a God. Measure of the Earth and the Moon During lunar eclipse, shadow cast by Earth is circular Earth is a sphere. As seen from Earth Erastothenes (276-194 BC): If the Sun is much farther away, its rays arrives on parallel lines. Anaxagoras’s problem is then given by the bottom diagram. Alexandria lies north of Syene by a latitude angle arctan(1/8) = 7.2o = 360o/50. Distance from Alexandria to Syene, 800 km, is 1/50 of the polar circumference around the world 2RE = 40,000 km RE = 6400 km. What Anaxagoras got as the distance to the Sun is actually the radius of the Earth! The Sun must be much farther away! Aristarchus (310-230 BC): During lunar eclipse, shadow has inferred diameter 3.7 times larger than 7.2o Alexandria diameter DM of the Moon. Thus, DM = 2RE/3.7. But 7.2o DM/rM = 0.5o = 0.009 rad rM = 2RE/[(3.7)(0.009)] Syene = 60 RE . (Crucial for Newton) If Sun is much farther than Moon, Sun is much bigger than Earth. Maybe Earth circles Sun. Eratosthene: size of the Earth Greek philosophers: constellations & star brightness Stars and planets Planets: cosmic wanderers Roots of Science in Mysticism Mystical concepts of elements & reasons for change Babylonian argument that water = “theory of everything” Source of all life between Tigris & Euphrates Capable of change from solid to liquid to gas Water, Fire, Earth, Air, and Aether/Quintessence (Greece) Water, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Wood (China) Numerology & association of metals/elements with planets Greece: Sun = gold, Moon = silver, Mercury = tin, Venus = copper, Mars = iron, Jupiter = asem, Saturn = lead (7 “planets” = 7 day week); quicksilver metal China: Mercury = water, Venus = metal, Mars = fire, Jupiter = wood, Saturn = earth Ptolomy’s geocentric model Aristarchus’ heliocentric theory Hipparcus’s parallax Ptolomy’s geocentric model: Planets retrograde motion Copernicus’ revolution Heliocentric model