* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Drake equation wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Fermi paradox wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
Ultimate fate of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Flatness problem wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
High-velocity cloud wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Lambda-CDM model wikipedia , lookup
Structure formation wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
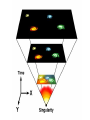
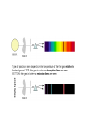
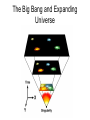
Beyond our Solar System There are probably more than 170 billion (1.7 × 1011) galaxies in the observable universe. Most galaxies are 1,000 to 100,000 parsecs in diameter and are usually separated by distances on the order of millions of parsecs (or megaparsecs). Elliptical Galaxies • 80% of galaxies are elliptical in shape • X-ray technology has discovered black holes and neutron stars in some elliptical galaxies. • Elliptical galaxies can be up to 2 trillion light years across and can contain up to 10 trillion stars Spiral Galaxy Artist rendition of Milky Way Barred Spiral Galaxy • Consist of curved arms radiating from a central, dense bulge • Milky Way (our galaxy) is a spiral galaxy • Our solar system lies on one arm (Orion Arm) Milky Way Galaxy • Consists of over 200 billion stars • 16,000 light years thick (central bulge) • 100,000 light years across (long end to end) • The arm that our solar system is in (Orion Arm) is about 30,000 light years long Irregular Galaxy • No true shape (irregular masses) • Generally faint in luminosity • Smaller and less massive than spiral galaxies Origin of the Universe Singularity According to the standard theory, our universe sprang into existence as "singularity" around 13.7 billion years ago. Our universe is thought to have begun as an infinitesimally small, infinitely hot, infinitely dense, something - a singularity. Big Bang Theory There are many misconceptions surrounding the Big Bang theory. For example, we tend to imagine a giant explosion. Experts however say that there was no explosion; there was (and continues to be) an expansion. Rather than imagining a balloon popping and releasing its contents, imagine a balloon expanding: an infinitesimally small balloon expanding to the size of our current universe. Electromagnetic Spectrum Visible Light • Represents a fraction of the different forms of energy on the electromagnetic spectrum. • The different wavelengths of visible light are different colors: – – – – – – – Red = longest wavelength Orange Yellow Green Blue Indigo Violet = shortest wavelength Emission Spectrum • Series of unevenly spaced lines of different colors and bright nesses. • These lines are arranged in the ROY G BIV sequence. • Each gas has its own unique emission spectrum (fingerprint). Absorption Spectrum • A continuous spectrum with dark lines ommitted from it. • Occurs when energy travels from a hotter object (sun’s interior) through a cooler gas (sun’s out layers). Absorption and Emission Spectrums Doppler Effect -- a perceived change in the frequency of a wave as the distance between the source and the observer changes. http://www.seed.slb.com/labcontent.aspx?id=11082&terms=doppler Fire Truck Sound.wav The Big Bang and Expanding Universe #1. The diagram below illustrates three stages of a current theory of the formation of the universe. A major piece of scientific evidence supporting this theory is the fact that wavelengths of light from galaxies moving away from Earth in stage 3 are observed to be 1. shorter than normal (a red shift) 2. shorter than normal (a blue shift) 3. longer than normal (a red shift) 4. longer than normal (a blue shift) #2. Which form of electromagnetic radiation has a longer wavelength than Microwaves? (1) ultraviolet (2) infrared (3) radio waves (4) microwaves #3. Which form of electromagnetic radiation has a wavelength of 1.0 × 10–3 centimeter? (1) ultraviolet (2) infrared (3) radio waves (4) microwaves #4. At which location will the highest altitude of the star Polaris be observed? 1. Equator 2. Tropic of Cancer 3. Arctic Circle 4. central New York State #5. Which star is cooler and many times brighter than Earth’s Sun? 1) Barnard’s Star 2) Betelgeuse 3) Rigel 4) Sirius