* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Waddesdon Bequest wikipedia , lookup
French Renaissance literature wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance in Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance music wikipedia , lookup
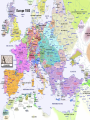
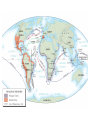
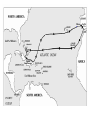
The Dark Ages Chapter 2 “Renaissance and Discovery” AP EUROPEAN HISTORY MR. RICK PURRINGTON MARSHALL HIGH SCHOOL Europe 1500 I. What was the Renaissance? A. “Re-birth” 1. new interest in the classics = politics, art, literature, architecture 2. Jacob Burckhardt – Ren gave rise to “new secular and scientific values” and the gradual release of the “full, whole nature of man.” 2. increased wealth, education, population II. The Evolution of the Renaissance A. Italy– center of the Ren 1. 15th C economy in Italy = strong a) “all roads lead to Rome” b) Venice = sea commerce = wealth c) Florence = wool trade, banking, art, architecture, literature d) Florentine banking families - Medici - “God’s bankers” = wealth and power Cosimo de’Medici Florence, Italy Basilica di Santa Maria del Fiore B. The Printed Word 1. 1454 - Johann Gutenberg a) first printing press – moveable type b) books now mass-produced c) Gutenberg Bible 2. Impact of the Printing Press a) stimulated literacy b) ideas and information spread III. Early Exploration 1300’s A. Marco Polo seeking trade routes w/Mongol Empire in China and India B. Mongol Empire declines, Islamic Ottoman Empire grows C. New routes, overseas trade is needed D. Problems: 1. little sea travel technology 2. maps weren’t extensive 3. knowledge of open sea travel was limited IV. Portugal Leads the Way EAST (end of 1400’s) 1. Port.’s geographic advantage 2. Prince Henry the Navigator a) wanted trade w/India, Africa 3. Shipping Technology a) compass, astrolabe b) cannons on ships for protection 4. Explorers’ motivations: a) God - Christianize Muslims “Crusading” b) Gold - import gold from West Africa, spices from India c) Glory – the Renaissance humanism 5. 1497 - da Gama rounds Africa, enroute to India http://www.learner.org/interactives/renaissance/exploration.html 6. 1500 – Port. lands in Brazil V. Spain Leads the Way WEST A. Christopher Columbus - Talented Italian Seaman 1. Convinced that Asia could be reached by sailing West 2. Portugal said no 3. Queen Isabella of Sp said yes 4.Discovered Caribbean isles, CentralAmerica 5. Called the people “Indians” 6. News of Columbus’ voyages spread quickly throughout Eu B. Impact of Columbus 1. Paved the way for: explorers – Megellan, Vespucci, and Spanish Conquistadors– Pizarro, Cortes 2. The Economy of Exploitation a) The Columbian Exchange of: - language, religion, foods, animals, spices, slaves, disease VI. Renaissance Thought A. Humanism 1. Studia Humanitatis – study of liberal arts or “humanities” - philosophy, politics, rhetoric, history 2. humans are between “angels and beasts.” 3. human potential for learning is limitless 4. the human body is divinely inspired) 5. Castiglione’s The Courtier 1) “The Renaissance Man” – has a strong background in many academic, physical, and spiritual subjects B. Civic Humanism and Political Philosophy 1) 1513 -- Machiavelli’s The Prince a) most widely read Ren book b) subject: how the ruler should gain, maintain, and increase political power c) humans are selfish d) “the ends justify the means” e) must be “a fox and lion” “For a man who, in all respects, will carry out only his professions of good, will be apt to be ruined amongst so many who are evil. A prince therefore who desires to maintain himself must learn to be not always good, but to be so or not as necessity may require. It is much more safe to be feared than loved.” “View what IS not what ought to be.” The Prince, Machiavelli VII. Renaissance Art and Sculpture A. New features brought energy and life to art 1. Embraced natural world, human emotion 2. Works characterized by: a) rational order b) symmetry c) proportionality d) linear perspective (3-D look) e) chiaroscuro – shading for naturalness B. Artists 1. Leonardo da Vinci (1452–1519) a) The Renaissance ideal, Mona Lisa, The Last Supper, Vitruvian Man 2. Raphael (1483–1520) a) The School of Athens 3. Michelangelo (1475–1564) a) David, The Pieta, The Sistine Chapel 10,000 sq. ft., 343 figures, 4 yrs to complete VIII. The Renaissance in Northern Eu A. Differences in the North 1. More religious, less secular 2. A combination of classic and religious virtues 3. Northern Humanists a) 1516-Thomas More Utopia 1. describes the ideal society 2. learning, social equality, shared profits, wars prevented w/gold 3. no greed, no corrupt institutions b) 1504-Erasmus The Education of a Christian Prince 1. study of Bible and classics can bring positive change 2. the goal is to live like Jesus Christ 3. challenged the Church