* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Digestive Anatomy
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Adjustable gastric band wikipedia , lookup
Hepatic encephalopathy wikipedia , lookup
Intestine transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Liver transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Liver cancer wikipedia , lookup
Cholangiocarcinoma wikipedia , lookup
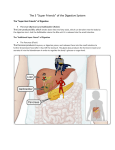
The Digestive System “alimentary canal” Overall Function Digestion is the chemical and physical breakdown of food into a form usable by cells. Organs of Digestive System MAJOR ORGANS • Mouth • Oropharynx • Esophagus • Stomach • Small intestine • Large intestine • Rectum ACCESSORY ORGANS • salivary glands • Tongue • Teeth • Liver • Gallbladder • Pancreas • Vermiform appendix Digestive Tract Also known as alimentary canal or gastrointestinal (GI) tract. It forms a tube that separates from digesting food from the body’s internal cavity. Layers of GI tract Mucosa – Inner layer of the lumen (open space) Submucosa – Made of connective tissue, glands, blood vessels and nerves Muscularis – Surrounds submucosa, smooth muscle that contains nerves that form part of the intramural plexus Serosa – Outermost layer made of connective tissue The Mouth • Lips – When closed form the oral fissure • Cheeks – Formed by muscle and adipose tissue • Hard & soft palate – Uvula suspends from soft palate • Tongue – Muscle movements aid in mastication The Mouth Salivary Glands • Pairs include parotids, submandibular, and sublingual • Secrete ~1L of saliva per day • Buccal glands in the mucosa lining produces a small amount of saliva The Teeth • Three main parts – Crown – Neck – Root • Deciduous teeth(20) are baby teeth • Permanent teeth(32) show up from 613 yrs The Pharynx • Deglutition is the act of swallowing a bolus, rounded mass of food and saliva from the mouth to the stomach. The Esophagus • ~10 inches longs • Sits posterior to trachea and heart • It is normally flatted in resting state • Each end is guarded be a sphincter – Upper esophageal (UES) – Lower (cardiac) esophageal (LES) • Esophageal hiatus is opening in diaphragm where esophagus passes – When enlarged can lead to hiatal hernia GERD- gastro esophageal reflux disorder, severe acid reflux and indigestion caused by weakened LES. The Stomach • Located directly below the diaphragm • Normally holds 1-1.5 L • 3 parts Esophageal hiatis fundus – Fundus (upper left) – Body (central) – Pyloris (lower) body • 2 sphincter – LES(cardiac) – Pyloric pyloris The Stomach • Gastric Mucosa, lining of the stomach contain many folds called rugae and depression called gastric pits • Cells in the stomach produce HCL and intrinsic factor • Intrinsic factor binds to B12 molecules keeping them from being broken down so they can be absorbed in the sm. Intestines The Stomach • Gastric muscles, muscularis, is made of longitudinal, circular and oblique layers. This gives it strong grinding power. The Stomach Overall Functions • Secrete gastric juices and intrinsic factor • Store partially digested food • Churn food with digestive juices and move it into duodenun • Limited absorption, alcohol, some H2O and some fats • Release hormones that regulate digestive functions • Destroy pathogenic bacteria The Small Intestine • ~6m in length • 3 parts – Duodenum- first section, shaped like a C – Jejunum- 2.5m, begins with abrupt turn – Ileium- last 3.5m • Small projections called villi line the sm. Intestine. – Each contain an arteriole, venuole and lacteal • Microvilli present on the villi increase the surface area of intestinal wall The Small Intestine • Secretion of digestive enzymes and absorption occur in small intestine • Small pockets at the base of the villi, called crypts, contain cells that reproduce rapidly • These cells push up and constantly replace older cells that are shed Large Intestine • 1.5-1.8m • 3 parts – Cecum- first 5-8cm – Colon • Ascending • Transverse • Descending • Sigmoid (s-shaped) – Rectum17-20cm • Anal canal has folds with a vein and artery • Hemorrhoids are enlargement of those veins – Anus is made up of two sphincters The Large Intestines Accessory Structures • Vermiform appendixthought to hold beneficial flora • Peritoneum- serous membrane that lines abdominal cavity • Mesentery- fan shaped part of peritoneum which attaches to small intestine • Omentum- attached to greater curvature of the stomach and is laced with fat deposits The Liver • Weighs ~1.5kg • Made of two lobes – Left lobe is smaller – Right lobe has 4 parts • Liver is made of small units called hepatic lobules The Liver • Blood enters the lobules from the hepatic portal system to be “cleaned” • The liver: – Destroys old RBCS, bacteria – Vitamins and nutrients are metabolized – Toxins are absorbed and detoxified – Bile formed collects in small bile ducts Bile Ducts • The right and left bile ducts emerge from under the liver to form the common hepatic duct • The common hepatic duct joins with the cystic duct (gallbladder) to form the common bile duct • Common bile duct empties into the duodenum Function of the Liver • Detoxify substancealcohol, medicines • Bile production • Metabolize fats, proteins and carbohydrates • Store substancesFe, vitamins A, B12, D • Bile salt released by liver aid in absorption of fats Gall Bladder • Main function is to store and concentrate bile • Contain tiny folds of rugae that contract to secrete bile during digestion • Jaudice is caused by a buildup of bile in the blood • Cholelithiasis is the formation of gallstones Pancreas • Fish shaped textured organ that is exocrine and endocrine gland • Rests below stomach on top of duodenum • Exocrine portion secrete digestive enzymes that collect in the pancreatic duct, that joins the common bile duct • Endocrine islets cells secrete insulin and glucagon directly into the blood