* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Endocrine System
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Adrenal gland wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
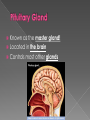
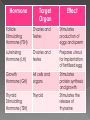
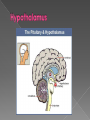
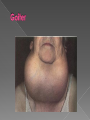
The endocrine system is made up of glands that release hormones into the blood. Hormones are chemicals that deliver messages throughout the body. Hormones act by binding to specific chemical receptors on cell membranes or within cells. Cells that have receptors for a particular hormone are called target cells. If a cell does not have receptors for a particular hormone, the hormone has no effect on it. Endocrine glands secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Exocrine glands secrete substances through tube-like structures called ducts. Ex: sweat, tears, and digestive enzymes Known as the master gland! Located in the brain Controls most other glands Hormone Target Organ Effect Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Ovaries and Testes Stimulates production of eggs and sperm Luteinizing Hormone (LH) Ovaries and testes Prepares uterus for implantation of fertilized egg Growth Hormone (GH) All cells and organs Stimulates protein synthesis and growth Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Thyroid Stimulates the release of thyroxine Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH): signals the kidneys to NOT absorb water from the blood When the blood has enough water or too much water, the pituitary will stop releasing ADH and the kidneys can begin filtering water from the blood again Caffeine is a diuretic. What does this mean? Also located in the brain above the pituitary gland Serves as a link between the nervous system and the endocrine system Produces and secretes a specific releasing hormone that controls the hormones that the pituitary gland secretes Located on top of the kidneys Release hormones that prepare for, and deal with, stress Fight or flight decisions Epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine These cause in increase in the heart rate and the rate of breathing They also activate sweat glands Increase blood pressure Stimulate the release of extra glucose, which is stored in the liver as glycogen The pancreas is both an exocrine gland and an endocrine gland As an exocrine gland, the pancreas releases enzymes that help digest food As an endocrine gland, the pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose Inside the pancreas, insulin is produced in clusters of cells called the islets of Langerhans The pancreas also releases glucagon, which stimulates the liver to break down glycogen into glucose When the body has enough of a particular hormone or a hormone’s job has been accomplished, the endocrine gland that creates that hormone shuts down. Compare this to a furnace that is set at a particular temperature. Type 1 Diabetes is a disorder where the pancreas does not make enough insulin If the pancreas does not make enough insulin, what will happen? The thyroid gland is located in the front of the windpipe called the (trachea) and just below the larynx or Adams Apple on the neck. The Thyroid gland regulates your (Metabolism) or your ability to break down food and use it for energy. The thyroid gland keeps your metabolism under control by thyroid hormones such as thyroxine. The thyroid gland produces thyroxine by extracting iodine from the blood. IODINE is needed to produce thyroxine Iodine is found in seafod, animal, plant foods, & table salt (sodium). A lack of thyroxine (iodine) can cause several problems as all cells in your body depend on thyroxine for cellular function. One condition is a swollen condition of the neck which is called Goiter. Goiter is caused by the thyroid enlarging or becoming swollen. SPOILER ALERT!!! The next slide is very disturbing! To combat this condition, the U.S.D.A. makes salt companies add iodine to their salt. Since the thyroid controls metabolism, What do you think “hypothyroidism” is? What about “hyperthyroidism?” Symptoms: No energy Loss of hair Overweight Overactive Bulging eyes ANOTHER DISTURBING SLIDE!! 4 tiny glands located on the back of the thyroid Releases calcitonin which causes the bones to absorb calcium