* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Seizure Terms
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
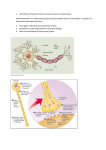
Epilepsy and Seizures Definition of seizures and epilepsy Epidemiology Classification of seizures Examples Diferential diagnosis Clinical Definition of Seizure Paroxysmal uncontrolled discharges of neurons within the central nervous system (grey matter disease). “These Paroxysmal episodes of brain dysfunction manifested by stereotyped alteration in behavior” Clinical manifestations of a seizure based on anatomy of the brain that is seizing Symptoms: sensory, motor, autonomic with or without loss of consciousness Epilepsy is a disease in which recurrent and unprovoked seizures occur spontaneously What are seizures? • Cellular definition: excessive or oversynchronized discharges of cortical neurons • GABA receptor mediates inhibition responsible for normal termination of a seizure • NMDA (Glutamate) receptor activation required for propagation of seizure activity NMDA Rcptr Activation Seizure Reduced GABA Rcptr function 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 4 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 Yaş Fokal Epilepsi Jeneralize Epilepsi EEG interpretation !! Seizure Classification Seizure terms Partial= focal region involved Generalized= whole brain Convulsions= shaking Seizure Phenotypes think of anatomy!! Cortex Central Sulcus Frontal Eye Field Visual Assoc. Cortex Brocas’s Speech Area Primary Visual Cortex Primary Auditory Cortex Sylvian Fissure Wernicke’s Speech Partial Seizures Homunculus Frontal Lobe Frontal Eye Field (Brodman’s 8) Lesion: deviation of eyes to ipsilateral side Sz: overstimulation->eyes to contralateral side Prefrontal Cortex (Brodman’s 9-12,46,47) Lesion: deficits in concentration, judgment and behavior Sz: agitation, odd behavior Broca’s Speech Area (Brodman’s 44,45) Lesion/Sz: expressive nonfluent aphasias Primary Motor Cortex (Brodman’s 4) Lesion: contralateral spastic paresis Sz: contralateral posturing/convulsions Temporal Lobe Hippocampal Cortex Bilateral lesions: inability to process short term to long term memory Sz: chronic seizures lead to deficits in short term memory Wernicke’s Speech area (Brodman’s 22) Lesion/Sz: loss of receptive speech, fluent aphasia Anterior Temporal Lobe Bilateral lesions: “Kluver-Bucy syndrome” of visual agnosia, oral tendencies, hyperphagia, hypersexuality, docility Sz: pts “freeze” and might have oral automatisms Primary Auditory (Brodman’s 41, 42) Bilateral lesion: cortical deafness Sz: auditory hallucinations Olfactory Bulb (Brodman’s 34) Lesion: ipsilateral anosmia Sz: olfactory and gustatory hallucinations Limbic System Means “border” in Latin Border between cortex and hypothalamus Involved with emotional behavior Fear/anger/sexual behavior Short term memory Includes: Hippocampus Fornix Mammilary bodies Ant. Nucleus thalamus Cingulate cortex Seizures involving the hippocampus can have clinical symptoms of poor short term memory and abnormal mood Parietal and Occipital Lobe Primary Sensory Cortex (Brodman’s 3,1,2) Lesion: contralateral hemihypestheisa and astereognosis Sz: contralateral sensory symptoms ie: tingling, heat Occipital lobe (Brodman’s 17) Lesion: contralateral hemianopsia with macular sparing Sz: flashing or colored lights in contralateral visual field Psychogenic non-epileptic seizures -PNES Non-epileptic seizures May be manifestation of conversion disorder, factitious disorder or malingering Features that may distinguish from epileptic seizures Pre-attack preparation, absence of post-ictal confusion “Disorganized” movements, pelvic thrusting, thrashing Bilateral convulsions without loss of consciousness Violent or goal-directed behavior, obscene language, Forcefull eye closure Tongue biting Time!!!!! Video EEG may help to diagnose