* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TERAPI BIOLOGIK (Kuliah Umum Psikiatri Mhs.tk
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Serotonin syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Chlorpromazine wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Atypical antipsychotic wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Antipsychotic wikipedia , lookup
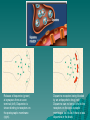
BIOLOGICAL TREATMENT dr. A.A.A.A. Kusumawardhani,SpKJ(K) 2009 Psychiatric treatment Comprehensive – Eclectic-Holistic Organobiologic Sociocultural Psychoeducative Therapy in Psychiatry Biological / Physical treatment: a. Drugs / Psycho-pharmacotherapy b. ECT/ Electro Convulsion Therapy c. Others Psychological treatment: - Psychotherapy individual/group - Psychotherapy - supportive - re-educative - re-constructive Psycho-pharmacotherapy PSYCHOTROPIC DRUGS > Major action at CNS : - Thinking process - Mood - Motoric function / behaviour Clinical effect Clasification: 1. 2. 3. 4. Antipsychotics/Neuroleptic/Major Tranquilizer Antidepresant Antianxiety/Anxyolytic sedatives/Minor Tranq. Antimanic/Mood stabilizer Antipsychotics Classification: * Typical DA phenothiazine & Nonfenothiazine * Atypical SDA # High Potency # Low Potency Pharmacokinetic of antipsychotics (1) Age : geriatric clearence Genetic : ethnics different metabolism Substance Abuse behaviour : * smoking metabolisms * alcohol metabolisms, liver function & nutrition Medical condition : * liver diseases, ex. Cirrhosis hepatis * Congestive Heart failureblood flow clearence Pharmacokinetic of antipsychotics (2) Enzyme inducers *carbamazepine, phenytoin, ethambutol, barbiturate Clearance Inhibitors * SSRI, TCA, beta blocker dll. Changes in binding protein * stress, hipoalbumin, hepatic/renal failure. Pharmacodynamic Mode of action : DA & SDA psychotics symptoms (hallucination, delusion, etc.) Dopamine Receptor Antagonis: * nigrostriatal system * mesolimbocortical system * tuberoinfundibuler system Nigrostriatal pathway Substantia Nigra to Striatum . Motor control . Death of neurons in this pathway can result in Parkinson's Disease Mesolimbic and Mesocortical pathways Ventral Tegmental Area to Nucleus Accumbens, Amygdala & Hippocampus, and Prefrontal Cortex . Memory . Motivation and emotional response . Reward and desire . Addiction . Can cause hallucinations and schizophrenia if not functioning properly Dopamine Pathway Tuberoinfundibular pathway Hypothalamus to Pituitary gland . Hormonal regulation . Maternal behavior (nurturing) . Pregnancy . Sensory processes Release of dopamine (green) at synapses from an axon terminal (left). Dopamine is shown binding to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane (right). Dopamine receptors being blocked by an antipsychotic drug (red). Dopamine can no longer bind to the receptors on the post-synaptic membrane, so it is as if there is less dopamine in the brain. Classification (chemical structure) - - Phenothiazines Aliphatic : Chlorpromazine, Promazine, Triflupromazine Piperidine : Thioridazine, Promazine, Piperazine : Fluphenazine, Trifluoperazine Classification (chemical structure) Thioxanthenes : Chlorprothixine, Thiothixene Butyrophenones : Haloperidol, Droperidol Dibenzoxazepine : Loxapine Dihydroindoles : Molindone Diphenylbutylpiperidines : Pimozide Side effects (1) Neurologic : *acute (acute extrapyramidal syndrome) # acathisia # acute dystonia # parkinsonism # Neuroleptic Malignan Syndrome *chronic # tardive dyskinesia Side effects (2) Cardiovascular effect * Orthostatic (Postural) Hypotension * Sudden Unexplained Death GIT * peripheral anticholinergic effects Liver, hepatology, renal, skin & eye Endocrinal dysfunction Sexual dysfunction Treatment Principal Initial gradually increase dosage --> optimal dose ( 1 – 3 weeks) Stabilisation (up to 8-10 weeks) Maintenance (months – years) Side effects management (1) SE Parkinsonism use antiparkinsons drugs, such as: * artane (trihexyphenidil) * congentin (benztropin) * diphenhydramin (benadryl) (do not use routinely) NMS : *stop antypsychotic *treat symptomatically *observe vital signs Side effects management (2) Tardive dyskinesia : * make a clear diagnosis ensure effective AP * use only minimal dose * caution in usage for children, geriatric, and patients with mood disorders * do regular examination for side effects * TD + give an informed consent, lower the dosage change drug * when TD getting worse stop the drug change/try Clozapin ANTIDEPRESANT Classification. * derivative of tricyclic AD Imipramin - Tofranil Amitriptilin- Laroxyl Amineptin - Survector * derivative of tetracyclic AD Maproptilin - Ludiomil Mianserin - Tolvon Antidepresant (1) •Monoaminoxidase Inhibitor MAOI & RIMA -moclobemide (Aurorix) •Serotonergic (SSRI) - Sertralin - Fluoxetine - Fluvoxamin - Paroxetin Antidepresant (2) Purpose: Heal / decrease depresive symptoms Mode of action : Increase NT concentration especially norepinephrin & serotonin Antidepresant (3) Side effects: 1. Hypotension (geriatric) 2. Cardio effects (EKG abnormality) 3. Otonomic symptoms 4. CNS effect 5. Allergy 6. hematology problems 7. psychological symptoms (manic, restlessness) Antidepresant (3) MAOI side effects: - hypotension & hypertension - hepatologic problem - otonomic - neurological (paresthesia,convulsion) - oedema - hematologic - psychologic disturbances - crisis hypertention Antidepresant (4) Treatment Principals: - start from low dosage therapeutical effect appears within 2 / 3 weeks - maintenance phase minimal 6 months & can last for 3 – 5 years Tricyclic Antidepressant Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor MAOI ANTIANXIETY CLASSIFICATION 1. Derivative of Benzodiazepine - diazepam bromazepam lorazepam clobazam alprazolam - valium lexotan ativan frisium xanax Buspiron -buspar 2. Derivative of Gliserol - meprobamat 3. Der. Of Barbiturate - phenobarbital Antianxiety (1) Purpose : Decrease anxiety - sedative effects - relaxation - amnesia - antiepilepsy Therapeutic Principal: - do not use high dosage - do not use more than 1 month Antianxiety (2) Side - Effects drowsiness headache dysarthri ataxia appetite dependent withdrawal effects MOOD STABILIZER Main purpose: control manic condition & prevent relapses Lithium : Indications: manic/depressive episode Effective doses : 0.8 – 1.5 mEq/l plasma level (start with 300 mg/day p.o) Antimanic (1) Side Effecs : - soft tremor - diarrhea & vomiting - fatigue & vertigo - ataxia & rough tremor - declining consciousness - convulsion - oligouria & anuria - oedeme Antimanic (2) “Mood Stabilizer” 1. Lithium salt Lithium carbonate - Priadel - Theralith 2. Others Carbamazepine - Tegretol Valproic Acid/Devalproate - Depakote ELECTRO CONVULSION THERAPY (ECT) Main Indication: Major Depression Electrify the brain (using 2 elektrodes placed on temporal region) convulsion like that of grandmal epileptic ECT (1) Preparation : - patient physical check up (Cardiovascular,pulmo,bones,brain) - Informed consent - fasting minimal 6 hours before ECT - prepare the patient to remain calm : distract their attention, give premedication - remove false teeth, jewelry, hair pin - nurse assistance for preventing luxasio/fracture ECT (2) Tools preparation : - ECT machine - wet cotton for underlying electrodes - oxygen tube & mask - mucous suction - drugs : coramine, adrenalin - rubber teeth holder - flat bed ECT (3) Execution : - Patient is laid down without pillow, in baggy hospital clothes - Rubber teeth holder Nurses hold : lower jaw/ head; shoulder; hip & knee - Doctor place the elektrodes tonic convulsion -->clonic convulsion apneubreath normally (important phase) ECT (4) Post ECT observation : - important - until vital condition become normal, still unconcious, usually falling asleep; sometimes restless & moving uncontrollably nurses must keep watching until the patient is fully councious. ECT (5) - after regaining consciousness, the patient often confused, disoriented and amnestic nurses help orientation and memory by communicating in stages, giving a calming and nonirritating environment. OTHER BIOLOGICAL THERAPY Light therapy Sleep Deprivation & Alteration of Sleep Schedules Psychosurgery Orthomolecular therapy Subcoma Insulin therapy Coma therapy Carbon Dioxide therapy Resource: Comprehensive Texbook of Psychiatry –Kaplan HI, Saddock BJ