* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Seedless Vascular Plants
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
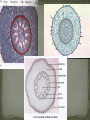
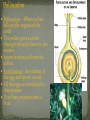
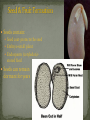
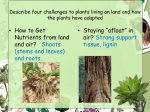
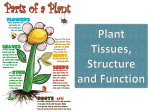
Multicellular, Eukaryotes Cell walls made of cellulose Waxy waterproof cuticle Autotrophs Photosynthetic with chlorophyll Vascular tissue Vascular Tissue- tubes that carry food, water and carbon dioxide throughout the plants Xylem-transport water Phloem-transports sugars made in the leaves during photosynthesis Some ancient plants are nonvascular Plants grow from the Apical Meristem at the root and stem tips of the plant This is a zone of cells undergoing mitosis (cell division) Have no seeds have spores –hard walled reproductive structures Vascular & non-vascular Usually moist environments Ex: Liverworts Hornworts Mosses Ferns Produce seeds Vascular See pg 568 Gymnosperm Conifers Reproduce with Cones Pollen cone Ovulate cone Seeds are in Cones Evergreen plants Needlelike leaves Pine, spruce, fir, redwood Three Main Parts Roots Absorb water Stem Hold up leaves and flowers Leaves Carry out photosynthesis Functions Absorb water and minerals from the soil Anchor the plant Epidermis Root Hairs- increase surface area, absorb water Cortex- can store food Endodermis-surrounds the vascular tissue Root cap-protection Apical Meristem- zone of cell division Vascular tissue is in Vascular Bundles Xylem-transport water Phloem-transport food Monocot Roots have xylem and phloem in a circle with a central pith Dicot roots have xylem in the shape of a star at the center Fibrous, Taproot, Prop Large underground roots store food beets, carrots, Adventitious roots- grow from the stem Function Support leaves & flowers Provide communication between leaves and roots Contains vascular tissue Xylem-water Phloem-food Types Herbaceous stems- green Woody stems Modified Stems can store food -this is an adaptation Celery Onion Bamboo shoots Sugar cane Vascular Tissue tube cells xylem and phloem Monocot Monocot stems-the vascular bundles scattered throughout the stem. Dicot stems-the vascular bundles form a circle in the cortex Dicot P Conifers and Angiosperm trees grow in thickness year to year. Secondary growth growing in thickness over years. X 1st year P New xylem is added yearly Last years dead xylem becomes a growth ring 2nd year X 3rd year Over time the outer portion of a stem develops bark protects the phloem (food) from damage and insects Function Site of Photosynthesis Large, flat surface area to trap light energy. Parts of a Leave Blade Petiole- stalk containing vascular tissue Veins- vascular tissue Cuticle-waxy coating Monocot Leaves have parallel veins Dicot leaves have a branching network of veins Epidermis – Outermost cell layer Mesophyll- contains chloroplasts Vein – contains xylem & phloem Stomata-mouth like openings on the underside of a leaf allow the exchange of CO2 and O2 gases with the air water vapor can be lost through open stomata Guard cells Tendrils - ivy Pitcher Plant –carnivorous plant Aloe Vera Cactus – water storage Food storage- lettuce, cabbage, spinach Alternation of Generations Ferns, mosses, conifers Evolutionary partners with insects Trade food for pollination Reproductive structure of plants Petal-colorful modified leaves that attract pollinators Pistil-female structure Ovary-egg producer Stamen-male structure Anther-produces pollen which contains sperm Sepal – supports petal Complete flower-has all 4 organs Monocot flowers- petals in multiples of 3 Dicot Flowers- petals in multiples of 4 or 5 ROOTS Fibrous Tap Branched veins LEAVES Parallel veins FLOWER Flower parts in 5’s Pollination – When pollen falls on the stigma of the pistil The pollen grows a tube through the style down to the ovaries Sperm is released from the pollen Fertilization - the joining of the egg and sperm occurs All the eggs are fertilized in this manner The Ovary matures into a Fruit Seeds contain: Seed coat-protects the seed Embryo-small plant Endosperm (cotyledon)stored food Seeds can remain dormant for years Cotyledon -the food storage organ found in seeds The embryo Monocotyledon - one embryo leaf Dicotyledon- two embryo leaves Seed coat Seeds are spread many ways: Wind Water Animals Propelled The beginning of development of the seed into a new plant Steps in germination Seed absorbs water to begin germination Embryo does respiration First root appears First leaves appears Photosynthesis begins Plants respond to Light Water by growing towards both Plants release hormones – chemical messengers for these responses Annuals- plants that live for one year Biennials-plants that live two years Perennials-plants that live for several years, producing flowers and seed periodically Deciduous Trees - lose their leaves in the fall