* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Molecular and Morphological Homologies PPT File
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
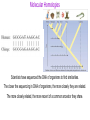
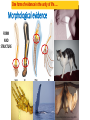
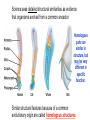
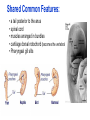
BELL RINGER 1. What is the difference between these two types of speciation paths? 2. What is indicated by the straight horizontal lines in the Punctuated graph? (why doesn’t the Gradual graph have those?) 3. What is indicated by the straight vertical lines in the Punctuated graph? 3/23/17 Today we are going to focus on Molecular and Morphological homologies as evidence of evolution. • Homology is similarity resulting from common ancestry. MOLECULAR HOMOLOGIES All living things have A,T,C,G in their DNA and ALMOST ALL organisms use the same codon chart to code for the same amino acids. This chart is showing how similar a certain protein is between various organisms. (The hemoglobin protein) Molecular Homologies Scientists have sequenced the DNA of organisms to find similarities. The closer the sequencing in DNA of organisms, the more closely they are related. The more closely related, the more recent of a common ancestor they share. The biochemistry (DNA) of a bat is much closer to that of a whale, than that of a bird. Why? The same technology used to determine paternity can be done to determine shared ancestry. Because bats and whales are mammals! Therefore, more closely related….. Bat Whale Bird One form of evidence in the unity of life….. Morphological evidence FORM AND STRUCTURE Science sees detailed structural similarities as evidence that organisms evolved from a common ancestor. Homologous parts are similar in structure, but may be very different in specific function. Similar structural features because of a common evolutionary origin are called homologous structures. Vestigial Structures These are structures that used to have a function, but no longer do….therefore suggesting evolution based VIDEO on new behaviors or environments Embryology is the study of organisms in embryonic stages. The embryo is one of the earliest stages of growth and development of both plants and animals. The shared features in the embryos of vertebrates suggests evolution from a distant common ancestor. Shared Common Features: • a tail posterior to the anus • spinal cord • muscles arranged in bundles • cartilage dorsal notochord (becomes the vertebral column) • Pharyngeal gill slits QUESTION: DISCUSS WITH YOUR GROUP: If you had two organisms in your lab with similar looking features, how could you find out if these structures are homologous or analogous? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P3GagfbA2vo CRASH COURSE VIDEO IN EVOLUTION