* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evidence for Evolution
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
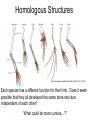
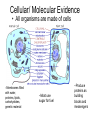
Wednesday May 5, 2010 Entry task (please write in your notebook) Natural selection is sometimes described as “survival of the fittest”. Lilly says that “fit” means “bigger, faster, stronger” like an Olympic athlete. • Do you agree or disagree? Why? Give an example. Now try this: • The DNA of a certain deer has a mutation that causes the deer to have white fur. – Is this a favorable trait? • When would each mutation be favorable? Unfavorable? a. Mutation that makes a mouse bigger b. Mutation that makes birds with toes that are slightly webbed Evidence for Evolution How do we know evolution happens? Fossil Record • Provides a peek at the past shows how living things have changed over the past 3.5 billion years. • May have bits missing, but fossil evidence clearly shows that life is old and has changed over time. Transitional Fossils Early whale ancestor. Land mammal, but clearly related to whales and dolphins based on specializations of ear. Gray Whale: lives today. The position of nostrils has changed over time. We would expect to see fossils that show intermediate forms. Geographic Distribution • Some species are only found in certain parts of the world, likely because they evolved there •Alligators in United States •Marsupials on the islands of Australia and New Zealand Geographic Distribution • Organisms show more similarity to species nearby than in similar climates but far apart. • Implies ancestry – Example: species on Galapagos Islands share more similarities with species on mainland South America than they do with species that live on other islands with similar climates across the world Homologous Structures • Similar characteristics due to relatedness Homologous Structures • The leaves look and function differently from each other, but are all derived from a common ancestral form. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Homologous Structures • Frogs, birds, rabbits, and lizards have different forelimbs, but they all share the same set of bones. Extinct, but shows common ancestry Homologous Structures http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/library/04/2/l_042_01.html Each species has a different function for their limb. Does it seem possible that they all developed the same bone structure independent of each other? “What could be more curious…?” Vestigial Organs • Traits that are not useful to an organism, but remain from a useful ancestral trait •Ear-wiggling muscles •Tail in human and all vertebrate embryos. •Appendix •Wisdom teeth •Hip bone of a whale Embryology/Development • Which of these is a pig embryo? Different vertebrates show striking similarities in early stages of development. http://lhs2.lps.org/staff/sputnam/Biology/U6Evolution/embryology.jpe Embryology/Development • Snakes have legged ancestors – Hind limb buds as embryos, but lose them before adulthood – Fossil evidence also shows snakes with hind limbs Cellular/ Molecular Evidence • All organisms are made of cells –Membranes filled with water, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, genetic material –Most use sugar for fuel –Produce proteins as building blocks and messengers Molecular Evidence • DNA: simple four-base code that provides instructions for all living things • All life is linked to a common ancestor • Different species share some of the same genes – Worms share 25% of their genes with humans! Molecular Evidence • The more similar the DNA of two living organisms, the more closely they may be to one another – Note: many other factors play a role as well • Activity: – study the amino acid sequence in the hemoglobin of humans, gorillas, and horses – use the data to show the similarities in DNA of these organisms