* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELL ENVIRONMENTS REVIEW SHEET
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
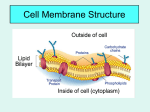
ENVIRO BIO CELL ENVIRONMENTS REVIEW SHEET 2014 NAME _______ANSWER KEY________________________ 1. What is diffusion? THE MOVEMENT OF MOLECULES FROM AN AREA OF HIGH CONCENTRATION TO LOW CONCRENTATION 2. Give three (3) examples of diffusion. PERFUME SCENT, SUGAR DIFFUSING IN COFFEE, FOOD COLORING IN WATER 3. Molecules move from a ___HIGH________________ concentration to a ____LOW_______________ concentration in order to reach a balanced state called __EQUILIBRIUM_______________________ 4. What is osmosis? Explain and be specific. OSMOSIS IS THE MOVEMENT OF WATER FROM AN AREA OF HIGH CONCENTRATION TO LOW CONCENTRATION ACROSS A CELL MEMBRANE 5. What is the difference between diffusion and osmosis? DIFFUSION IS THE MOVEMENT OF ANYTHING FROM HIGH TO LOW CONCENTRATION. OSMOSIS IS THE MOVEMENT OF WATER SPECIFICALLY FROM HIGH TO LOW CONCENTRATION ACROSS A CELL MEMBRANE. 6. TRUE OR FALSE: When making popcorn, the “scent molecules” are highly concentrated inside the package while being popped. When you open the package and release the molecules, hat would be an example of osmosis. Explain whether this statement is true or false and WHY. THIS IS FALSE BECAUSE IT DOES NOT TALK ABOUT WATER, WHICH IS OSMOSIS. THIS IS AN EXAMPLE OF DIFFUSION. 7. The movement of water from a greater to lesser concentration through a semi-permeable membrane is an example of what? OSMOSIS 8. Define “semi-permeable”. SOME THINGS CAN ENTER, NOT EVERYTHING Define “permeable”. EVERYTHING CAN ENTER Define “impermeable”. NOTHING CAN ENTER Directions: Label each statement with either “ISOTONIC” “HYPOTONIC” OR “HYPERTONIC” for questions #9-11. 9. If there is more water on the outside of the cell than inside, we would say that it is…. HYPOTONIC 10. If there is 92% water inside the cell and 92% water outside the cell, then it would be considered…. ISOTONIC 11. There is an equal distribution of water inside as there is outside of the cell…. ISOTONIC 12. Define the word “homeostasis”. A STEADY, STABLE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT 13. Give three examples of homeostasis: a. SWEATING TO COOL OFF b. SHIVERING TO WARM UP c. DRINKING WATER WHEN DEHYDRATED 14. Use the diagram from your notes to label the cell membrane: Labels: head, tail, hydrophilic, hydrophobic, phospholipid, protein, bilayer PROTEIN HEAD (HYDROPHILIC) TAIL (HYDROPHOBIC) BILAYER PHOSPHOLIPID 15. What are the functions of the cell membrane? Name two. a. REGULATE MATERIALS THAT ENTER AND EXIT b. PROVIDE SHAPE AND SUPPORT 16. What is a “phospholipid bilayer”? IT IS A DOUBLE LAYER MEMBRANE MADE OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS 17. Which part of a phospholipid mixes with water? THE HEAD 18. Which part of a phospholipid does not mix with water? THE TAILS 19. Define “hydrophilic”. (use online activity 6.2) MIXES WITH WATER 20. Define “hydrophobic”. (use online activity 6.2) DOES NOT MIX WITH WATER 21. What is “facilitated diffusion” and what molecules need to use it? FACILITATED DIFFUSION IS THE MOVEMENT OF MOLECULES ACROSS THE MEMBRANE THROUGH SPECIAL TUNNELS IN PROTEINS, FROM HIGH TO LOW CONCENTRATION. THIS IS PASSIVE TRANSPORT, AND DOES NOT REQUIRE ENERGY. 22. Does diffusion use energy from the cell? NO 23. Does osmosis use energy from the cell? NO 24. Does facilitated transport use energy from the cell? NO 25. Does active transport use energy from the cell? YES 26. Define active transport and why does a cell need to do this? ACTIVE TRANSPORT IS THE MOVEMENT OF MOLECULES UP THEIR CONCENTRATION GRADIENT, FROM LOW TO HIGH CONCENTRATION, AND THIS REQUIRES ENERGY 27. List the two TYPES of active transport discussed in class. ENDOCYTOSIS_____________________________ EXOCYTOSIS______________________________ 28. Which type of active transport moves materials into the cell? ENDOCYTOSIS 29. Which type of active transport pushes materials out of the cell? EXOCYTOSIS 30. In active transport, molecules go from an area of ___LOW____________ concentration to an area of __HIGH__________ concentration, which is _____UP_______ the “concentration gradient”. 31. In passive transport (diffusion, osmosis, facil. diffusion), molecules go from an area of ____HIGH___________ concentration to an area of ____LOW____________ concentration, which is __DOWN___________ the “concentration gradient”. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Directions: Name the tonic (isotonic, hypertonic, hypotonic), draw arrows to show which way the water moves, and answer the questions. 70% water 80% water 50% water 70% water Tonic?: ISOTONIC Which way does water go? BOTH DIRECTIONS Result in BIG words: DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM Tonic?: HYPOTONIC Which way does water go? INSIDE CELL Result in BIG words: PLASMOPTYSIS (ONLY ANIMAL CELLS) 10% salt 95% water (plant cell) Tonic?: HYPERTONIC Which way does water go? OUTSIDE OF CELL Result in BIG words: FLACCID (“WILT”) PLASMOLYSIS Tonic?: ISOTONIC Which way does water go? BOTH WAYS Result in BIG words: DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM HOMEOSTASIS Salt Water Red Blood Cell Tonic?: HYPERTONIC Which way does water go? OUTSIDE OF CELL Result in BIG words: FLACCID (“WILT”) PLASMOLYSIS 70% water 70% water Egg without shell