* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Area of a circle wikipedia , lookup
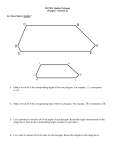
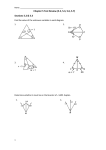
SEVEN CIRCLES In here there are activities for years 7 to 9. Each year develops a different aspect. Year 7 Constructing the 7 circles Finding shapes Properties of shapes Using notation A CONVERSATION on POLYGONS SEVEN CIRCLES Before we start you are going to have a 2 minute conversation. With you partner discuss as many properties of as many different polygons that you can recall. After two minutes we will discuss and list what you have found. Try to use the mathematical language on the next slide. Objective: To be to construct the 7 circles and to be able to discover polygons from circles and to use correct notation (you may use colour as well) and mathematical language to describe them. Have a go at reproducing this pattern. Use a radius of 6cm, starting from the centre of the A3 paper. What properties does the 7 circle pattern have? Using the points where the circles meet as vertices, find & draw these polygons. Equilateral Triangle Hexagon Isosceles Triangle Rectangle Right Angled Triangle Trapezium Extension Kite Right Angled Trapezium Pentagon Angles: Sum of the exterior angles 3 equal angles each ___degrees No equal angles Opposite angles are equal 4 equal angles each ___degrees Right Angle One pair of equal angles 5 equal angles each___degrees All angles add to 1 pair of opposite angles are equal 6 equal angles each___degrees Sides: One pair of parallel sides Names of Shapes: Two pairs of parallel sides Two pairs of opposite sides are equal Triangles Kite Isosceles Rhombus Right Angled Triangle Hexagons Scalene Equilateral Triangle Pentagons Quadrilaterals Regular Square Parallelogram Rectangle Trapeziums Total number of sides Conventions: One pair of adjacent sides are equal Two pairs of adjacent sides are equal No sides are equal 2 sides are equal All sides are equal Diagonals: Use arrows to show lines are parallel Diagonals cross at right angles Use marks to show lines of equal length Diagonals are of equal length Use arcs to show angles are equal Diagonals bisect each other Use this to show a right angle Symmetry: Lines of Symmetry Order of Rotational Symmetry Year 8 Constructing the 7 circles Finding shapes Proving the properties of shapes Using notation A CONVERSATION on POLYGONS SEVEN CIRCLES Before we start you are going to have a 2 minute conversation. With you partner discuss as many properties of as many different polygons that you can recall. After two minutes we will discuss and list what you have found. Try to use the mathematical language on the next slide. Objective: To be to construct the 7 circles and to be able to discover polygons from circles and to prove why that property is true. Have a go at reproducing this pattern. Use a radius of 6cm, starting from the centre of the A3 paper. Using the points where the circles meet as vertices, find & draw these polygons. Without using a ruler or protractor write down as many properties of the polygon as you can and explain how you know that property is true. Use correct notation and mathematical language (see next slide). Equilateral Triangle Hexagon Isosceles Triangle Rectangle Right Angled Triangle Trapezium Kite Right Angled Trapezium Pentagon Any other shapes? Angles: Sum of the exterior angles 3 equal angles each ___degrees No equal angles Opposite angles are equal 4 equal angles each ___degrees Right Angle One pair of equal angles 5 equal angles each___degrees All angles add to 1 pair of opposite angles are equal 6 equal angles each___degrees Sides: One pair of parallel sides Names of Shapes: Two pairs of parallel sides Two pairs of opposite sides are equal Triangles Kite Isosceles Rhombus Right Angled Triangle Hexagons Scalene Equilateral Triangle Pentagons Quadrilaterals Regular Square Parallelogram Rectangle Trapeziums Total number of sides Conventions: One pair of adjacent sides are equal Two pairs of adjacent sides are equal No sides are equal 2 sides are equal All sides are equal Diagonals: Use arrows to show lines are parallel Diagonals cross at right angles Use marks to show lines of equal length Diagonals are of equal length Use arcs to show angles are equal Diagonals bisect each other Use this to show a right angle Symmetry: Lines of Symmetry Order of Rotational Symmetry Year 9 Constructing the 7 circles Finding shapes Finding Perimeters & Areas Using notation SEVEN CIRCLES A CONVERSATION on POLYGONS Before we start you are going to have a 2 minute conversation. With you partner recall how to find the perimeter and area of as many different shapes as you can. After two minutes we will discuss and list what you have found. Objective: To be to construct the 7 circles and find the area and perimeter of the polygons listed below. Have a go at reproducing this pattern. Use a radius of 6cm, starting from the centre of the A3 paper. What is the area and circumference of on circle. (Show all working). C B A D Using the points where the circles meet as vertices, find & draw these polygons. Without using a ruler or protractor find the lengths of each side of the shape and their angles. Now find the perimeter and area of these polygons Equilateral Triangle Hexagon Isosceles Triangle Rectangle Right Angled Triangle Trapezium Kite Right Angled Trapezium Pentagon Any other shapes? Extension Find the above in terms of 𝜋 & 𝑟 . Find the perimeter & area of A, B, C & D. Year 10 Constructing the 7 circles Finding shapes Finding Equations of lines Using notation SEVEN CIRCLES A CONVERSATION on POLYGONS Before we start you are going to have a 2 minute conversation. With you partner recall the general equation for a straight line, what m & c represent and how to find the equation of a linear line. After two minutes we will discuss and list what you have found. Objective: To be to construct the 7 circles, draw in a set of axes and find the equation of the lines that are required to make the shape. Have a go at reproducing this pattern. Use a radius of 6cm, starting from the centre of the A3 paper. Draw in the axes & think carefully about the numbers that go on the axes. (Surds perhaps). Using the points where the circles meet as vertices, find & draw these polygons. Without using a ruler or protractor find the lengths of each side. Now find the equation of the lines that make up the sides of the polygonEquilateral Triangle Hexagon Isosceles Triangle Rectangle Right Angled Triangle Trapezium Kite Right Angled Trapezium Pentagon Any other shapes? Extension Place the origin not at the centre. Year 11 Constructing the 7 circles Finding areas and perimeters of shapes made from curves Using notation SEVEN CIRCLES A CONVERSATION on POLYGONS Before we start you are going to have a 2 minute conversation. With you partner recall the general equation for a straight line, what m & c represent and how to find the equation of a linear line. After two minutes we will discuss and list what you have found. Objective: To be to construct the 7 circles, draw in a set of axes and find the equation of each circle. Have a go at reproducing this pattern. Use a radius of 6cm, starting from the centre of the A3 paper. Draw in the axes & think carefully about the numbers that go on the axes. Find the equation of each circle. Extension Place the origin not at the centre. OTHER IDEAS PROBABILITY PROBABILTY - the 7 circles are now a dart board, where A is 12 points, B is 6 points, C is 3 points and D is worth 1 point. What assumption(s) do you have to make? Work out the following probabilities – P(A) = P(B) = P(C) = P(D) = P(not 12 points) = C B A D You have 2 throws of a dart and add the totals, find these probabilities – P(12) = P(square number) = P(prime) = P(multiple of 3) = Extension: You have 3 throws of the dart, find these probabilities – P(36) = P(21) = P(minimum points) = P(12) = P(10) = VECTORS Find i) The following vectors ii) Their length VECTORS A I H J b G N F a B K O L E OB = IJ = BD = HA = OE = FM = JB = AB = BF = A vector parallel to GM Find the angle between these pair if vectors – c M OK = C D OI & OJ KB & BA ON & OF ML & MI