* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Benzodiazepines
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of proton pump inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Effects of long-term benzodiazepine use wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
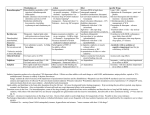
S.M.A.R.T. Dental Nursing Sedation Pharmacology of Benzodiazepines Day 3 Mr J. Henry Also see chapter Advanced Dental Nursing The ideal sedative agent Alleviate fear and anxiety Be easy to administer Be quickly effective Not suppress protective reflexes Be free of side effects Be predictable in both action and duration Be quickly metabolized and excreted Not produce active metabolites Have a half life of approx. 45-60 minutes Pharmacology of Benzodiazepines Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics – what the drug dose to the body – what the body does to the drug Pharmacodynamically benzodiazepines are all the same. Differences are due to: • Affinity for receptors (potency) • Half Life • Activity of metabolities Principle clinical effects: Anxiolysis Anticonvulsant Slight Sedation Reduced Attention Amnesia Intense Sedation Muscle relaxation Anaesthesia Mr J Henry 28/11/2015 1 Anxiolysis • • • Low doses Can be subtle Basis of oral anxiolysis without sedation NOT ANALGESIC! Anticonvulsant • • • Prevent and terminate convulsions Used in status epilepticus (can give midazolam intramuscularly but not diazepam) Local anaesthetic overdose Sedation • • • • • • Slight at low doses Intense at higher doses Decreased response to a constant stimulus Reduced attention Will lead to sleep if left un-stimulated Disinhibition Amnesia • • • • • Most intense with iv sedation Anterograde amnesia Intense for first 20/30 mins Variable duration but up to several hours Especially good with midazolam Muscle relaxation • • • • Central effect Depression of spinal reflex activity Partly responsible for respiratory depression Reduces trismus Anaesthesia • • Too large or too rapid (bolus) dose Very careful in elderly patients Mr J Henry 28/11/2015 2 GABA Gamma aminobutyric acid • • • Endogenous inhibitory neurotransmitter Mediates pre-synaptic inhibition Synthetised and stored in pre-synaptic nerve endings Action of GABA GABA attaches to the receptor site The chloride channels open Chlorine Ions enter Reduced activity of the post synaptic neuron Benzodiazepine Actions Benzodiazepines potentate the effect of Gamma Amino Butyric Acid (GABA ) by attaching to adjacent receptor sites in the Brain and CNS. The resulting increase the influx of inhibitory Chlorine ions into the nerve cells reduces the excitability of the nerve cells. The Chloride ions entering the cell making the resting membrane potential more negative. This makes it even more difficult to fire an action potential so reducing: polysynaptic transmission depressing the uptake of sensory information Properties of Benzodiazepines Rapid absorption from most sites Onset of sedation is smooth and rapid Very Lipophilic - readily taken up by the brain, liver and other fatty tissues Greater volume distribution in obese individuals leading to an increase in half life Metabolism of Benzodiazepines Broken down in the liver Some have metabolites which are biologically active (des methyl diazepam) a metabolite of diazepam has a longer half life than diazepam Mr J Henry 28/11/2015 3 Therefore entero-hepatic recirculation with des methyl diazepam at 9-12 hours may cause resedation Half Life Half life Midazolam 2-4 hours Half life Diazepam 12-24 hours Phases and Half Life Phases and Half Life Elimination half life is the time required for the drug concentration in the blood to half. Redistribution half-life is the time required for the initial peak level in the tissues to half Side effects of Benzodiazepines Respiratory Depression • • • CNS depression and muscle relaxation Decreased cerebral response to rise in CO2 Synergism with other CNS depressants Mr J Henry 28/11/2015 4 • • • • More common in: In patients with pre-existing respiratory disease Elderly When a second centrally acting drug has been used Cardiovascular effects • • • • • Reduction of BP by decreasing vascular resistance (15-33% midazolam) Compensatory rise in heart rate via baroreceptor response Cardiac output is unaffected Insignificant in fit patient (within 10% of norm) Considered cardiostable for poor risk patients in general anaesthesia. Drug interactions • • • • Synergism with other CNS depressants e.g. alcohol, opiates, antihistamines,tranquillisers. H2 receptor blockers ( cimetidine “tagamet”) inhibits the metabolism of benzodiazepines Cisapride (“Prepulsid”) Motility stimulant Baclofen,tizanadine( muscle relaxants) increased sedative effect Sexual Fantasy • • • • Males and females Usually dentist and patient opposite sex Where higher doses of midazolam are given > 0.1 mg/kg Chaperone mandatory Midazolam Formulation IV injection - clear ampoule Recommended Mr J Henry 28/11/2015 5mg in 5ml. (as per NPSA report) 10mg in 5ml (no longer used ) 5 10mg in 2ml. - too concentrated Properties Potent imidazobenzodiazepine 3-4 times as potent as diazepam Water soluble at pH ,4.0 Lipid soluble at physiological pH (can pass across the blood brain barrier) No thrombophlebitis or pain on injection Onset in one arm brain circulation but full clinical effect takes several minutes Route of administration. IV,IM, oral, rectal, intranasal, sublingual High first pass metabolism 97% protein bound (only 3% drug active) Pregnancy and Aging affects protein binding Protein binding is proportional to age Elderly especially sensitive to effects due to decreased protein binding <5mg in >60 year olds Effect of Aging Altered drug distribution Decreased total body water Increased total body fat Decreased serum albumin Altered hepatic metabolism Decreased mass, flow and enzyme activity Altered renal excretion Decreased flow, filtration rate Side effects of Midazolam Hiccoughs Nausea and vomiting Coughing “Over-sedation” Headache Drowsiness Local reactions eg. pain on injection Mr J Henry 28/11/2015 6 Midazolam Elimination half life 1.7 to 2.3 hrs ( 1.9hours) Broken down in the liver ( hydroxylated) Clinical working time is ~45 minutes Excreted by the kidneys (as glucuronide) Pharmacokinetics may be affected by renal and /or hepatic disease Midazolam – Drug interactions The drugs below Inhibit metabolism of midazolam resulting in increased plasma concentration and increased sedation effect Antibacterials Erythromycin, clarithromycin, quinupristin/dalfopristin and telithromycin Antifungals Itraconazole, ketoconazole and possibly fluconazole Antivirals Nelfinavir, Ritonavir ( Anti-HIV drugs) + Ca Channel blockers Diltiazem, Verapamil Midazolam Costs 10 Ampoules 50 Ampoules £ 9.95 £48.00 Midazolam overview + + + + - Good anxyiolsis Good amnesic Good hypnotic Short duration of action ( < 4 hours) Risks of respiratory depression Mr J Henry 28/11/2015 7 Diazepam Formulations Diazemuls 10mg. In 2ml. white lipid emulsion Diazepam 10mg. In 2ml. In brown ampoule Maximum dosage 20mg. Dissolved in Propylene Glycol - painful to inject Must use large veins in the ACF Maximum dosage 20mg. Diazepam Properties Mainly historical interest Non water soluble Dissolved in organic solvents or emulsified in soya bean oil Pain on injection and risk of thrombophlebitis Clinically significant metabolities ( des methyl diazepam half life 56 hours) Long half life 30 hours Mr J Henry 28/11/2015 8 Diazepam Route of administration. IV, oral Rebound sedation often seen (enterohepatic recirculation, broken down in liver, absorbed into gall bladder and secreted into duodenum in the next meal) Still recommended for termination of convulsions Oral diazepam useful for anxiolysis night before treatment Diazepam – Drug Interactions Antibacterials Antivirals Ulcer Healing Drugs Isoniazid inhibits metabolism Rifampicin increases metabolism Ritonavir ( Anti-HIV drugs) Increases plasma concentration ( risk of extreme sedation ) Omeprazole metabolism inhibited , increased plasma concentration Overview Diazepam Best anxiolytic, poor amnesic Minimal CVS depression Irritant to veins Long duration of action ( > 12 hours ) Active metabolites which prolong action Patient can re-sedate Midazolam Best amnesic, good hypnotic Some respiratory depression Not irritant - small veins Short duration ( < 2 hours ) No active metabolites Better recovery Can produces GA. Too rapid administration Mr J Henry 28/11/2015 9 Temazepam Formulation 10mg or 20mg or 10mg in 5ml tablets elixir Temazepam Properties Rapidly acting oral benzodiazepine Acts in 20-30 minutes Peak blood levels 2 hours Useful for night before or light sedation Controlled Drug (schedule III) Mr J Henry 28/11/2015 10 Temazepam Dosage 12 – 18+ years 20 - 40mg 30 minutes prior to treatment (10 mg night before treatment) Temazepam – Drug interactions Disulfram (used in treatment of Alcohol dependence) metabolism of temazepam inhibited , increased plasma concentration Increased sedation effect Overview Temazepam + + + + - Good hypnotic Reasonably good anxiolysis Short duration of action ( < 4 hours ) Similar 1/2 life to Midazolam Some dysphoric reactions in young adults and children Mr J Henry 28/11/2015 11 Flumazenil – Anexate Specific Benzodiazepine antagonist Essential requirement anywhere Benzodiazepine sedation is used effective reversal for both oral and IV benzodiazepine sedation. Flumazenil Formulation IV injection - clear ampoule 0.5mg in 5 ml. Action of ANNEXATE Anexate blocks the Benzodiazepine receptor site This prevents the synergistic effect The Chlorine channel reduces to its former dimension The sedative activity returns to normal Flumazenil Properties Benzodiazepine antagonist Reverses the receptor effects of Bzs No intrinsic activity but high receptor affinity Mr J Henry 28/11/2015 12 50 minute half life IV use but can be administered orally. Not recommended for routine reversal Flumazenil Dosage and Administration 0.2mg IV over 15 seconds then wait 1 min 0.1mg IV every 60 sec. until recovered. Maximum dose 1.0mg. - Two ampoules Flumazenil Prices 1 Ampoule £ 26.00 5 Ampoules £ 110.00 Flumazenil Important notes •Only for use in Emergencies •Not economic for routine use •Reawakening is rapid •Half life short - wears off after approx. 15 min. •Re-sedation can occur if original sedative was long acting. Must continue to monitor patients. •Can cause acute withdrawal reaction in habituated patients. •Can precipitate seizures in epileptic patients on long term benzodiazepine therapy. Mr J Henry 28/11/2015 13 Oral Sedation Midazolam Formulation 2mg in 1ml Solution VERSED Syrup Roche *Only licensed and sold in USA alternative I.V. preparation given in oral drink Dosage 0.5mg / kg body weight Childs weight easy calculation = ( Age + 4 ) x 2 ( up to maximum dosage 20mg ) Kg 30 minutes prior to treatment Diazepam Formulation 2mg, 5mg, 10mg or or 2mg in 5ml 5mg in 5ml tablets Solution Solution Dosage 2 – 5 years 6 – 12 years 12 – 18 years 2.5 mg 5 mg 10 mg Given 30mins - 1 hour prior to treatment Mr J Henry 28/11/2015 14 Temazepam Formulation 10mg or 20mg tablets or 10mg in 5ml elixir Temazepam Dosage 12 – 18+ years 20 - 40mg 30 minutes prior to treatment (10 mg night before treatment) Mr J Henry 28/11/2015 15 Intra-Nasal Sedation with midazolam MAD - Mucosal Atomization device: Device designed to allow emergency personnel to delivery nasal medications as an atomized spray. Broad 30-micron spray ensure excellent mucosal coverage. Dose 1ml in each nostril (5mg in 1ml solution) Midazolam Compared to oral medications, intranasal medication delivery results in: Faster delivery to the blood stream Higher blood levels No destruction by stomach acid and intestinal enzymes No destruction by hepatic first pass metabolism Other Points: Nasal drug delivery is convenient and easy, but it may not always be effective. Nasal drug delivery cannot completely replace the need for injections. Being aware of the limitations and using the correct equipment and drug concentrations will assist you in predicting times when nasal drug delivery may not be effective. Mr J Henry 28/11/2015 16 Take away lessons for nasal midazolam: Dose and volume: Higher concentration required - use 5mg/ml IV solution. Dosing calculations are difficult: Use a predefined age or weight based table to determine dose. Deliver immediately on decision to treat: Atomize into nose with MAD, then begin standard care. Efficacy: No quite 100% effective so failures with nasal may need follow-up with IV therapy. Adults 10 mg Midazolam Can be USED ALONE OR PRE IV SEDATION Mr J Henry 28/11/2015 17