* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Mr. Gutierrez`s social studies website!
Environmental determinism wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
History of geography wikipedia , lookup
Map database management wikipedia , lookup
Early world maps wikipedia , lookup
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
Counter-mapping wikipedia , lookup
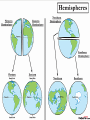
Studying Geography Chapter 2, Lesson 1 Displaying the Earth’s Surface ► Globes – Spherical model of the Earth More accurate than maps Show true distance and direction. ► Maps – flat drawings of all or parts of the earth’s surface Can show political borders, population density, or even voting results. Can be accurate for smaller areas. Hemispheres ► Hemisphere – half spheres of the world used to separate North, South, East, and West. ► Equator – circles the middle of the Earth like a belt. Separates the Northern Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere. ► Prime Meridian – like the equator but running north to south. Separates the Eastern and Western Hemisphere. Finding Places on the Earth ► Latitude – circle the earth parallel to the equator. The Equator is 0 degrees latitude. The poles are 90 degrees. ► Longitude – Circle the globe from the north pole and south pole. Prime Meridian is 0 degrees longitude. ► ► ► This grid system makes absolute location possible. Minutes are also used to help determine the location. EX: The Empire state building is located at latitude 40° 44` North and longitude 73° 59` West. 40 degrees 44 minutes North and 73 degrees 59 minutes West. Projections ► Projection – a way of showing the round Earth on a flat map. ► Mercator Projection – Land size and distance appear distorted ► Robinson Projection – a truer picture of the land size and shape. North and South poles are extremely distorted. ► Winkel Tripel Projection – Most closely resembles the globe model. Projections ► Mercator Projection – Land size and distance appear distorted Projections ► Robinson Projection – a truer picture of the land size and shape. North and South poles are extremely distorted. Projections ► Winkel Tripel Projection – Most closely resembles the globe model. What are the Five Themes of Geography? ► Location Where is it? ► Place What’s it like there? ► Human/Environment Interaction What’s the relation between humans and their environment? ► Movement How and why are places connected with one another? ► Region How and why is one area similar to another? Location Where is it? ► Absolute Location refers to the exact location of something. Ex: We can use longitude (North/South) and latitude (East/West) to identify where something is exactly on a map or globe. We can also use street addresses to locate an exact location in a city or town. ► Relative Location refers to where something is based on where something else is. Ex: The Miami Lakes Fire Department is next to the Miami Lakes Library. Place What’s it like there? ► Places can be described by two kinds of characteristics: ► Physical Characteristics describe a place based on it’s natural environment. Ex: Landforms, bodies of water, climate, soil, vegetation, animal life, etc. ► Human Characteristics describe a place based on human ideas and actions. Ex: Highways, buildings, parks, etc. Human/Environment Interaction ► This theme answers the question, “What is the relationship between humans and the environment?” Three concepts are involved here: ► Human depend on the environment: The natural environment is made up of living and non living things. Humans depend on this for food, shelter, and clothing. Human/Environment Interaction ► Humans modify the environment: Humans change an environment to meet their needs. Ex: Aqueducts, irrigate fields, create canals, build schools, homes, etc. ► Humans adapt to the environment: Humans adapt to circumstances in the environment Ex: People use Air Conditioners in places that are very hot, and heaters in places that are Movement How and Why are places connected with one another? ► Relationships between people in different places are shaped by constant movement of: Ideas Materials People Regions How are areas similar? Different? ► Physical Characteristics Climate, soil, natural vegetation. Ex: Mountain peaks, canyons, deserts, etc. ► Human Characteristics Economic, social, and cultural characteristics. Ex: New England, The South, The Midwest, The Bible Belt, etc. ► Boundaries can be vague (unclear) This is because two different regions can overlap with each other. Regions also do not have to be directly next to each other or simply located in one spot. The Six Essential Elements What are the Six Essential Elements of Geography? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. The World in Spatial Terms Places and Regions Physical Systems Human Systems Environment and Society Geography and its Uses World in Spatial Terms ► This element shows the world and places using maps and space. ► Absolute and Relative Location ► It is similar to Location in the Five Themes. Places and Regions ► This element goes along with the people in certain places and regions. Ex if a place is incredibly suited for farming, this activity may be the center of peoples lives in that area. Physical Systems ► Physical Systems can change the surface of the Earth. ► Animals and Plant life must live together in order to survive. ► The Shape of the world around people also effects the way they live. Ex: You can’t ride your bike in the water, or go swimming on a mountain top. Human Systems ► Like Physical Systems, Humans can change the geography around them. Ex: We can make a big river smaller by building a dam, or irrigate a field to bring water into an area that didn’t originally have water. Rome built aqueducts to bring water into its cities and town. Environment and Society ► Humans are affected by their environments and vice versa. Humans can grow trees to provide more oxygen. (Humans affecting the environment) The weather is very cold so humans must wear warmer clothing to survive.(environment affecting humans) The Uses of Geography ► Understand the relationship among people, places, and environments over time. ► Understanding the past and preparing for the future. Ex: In the past we saw the damage a hurricane could do. So to prepare for a storm like that, we build homes that can withstand the force of those winds to safely get by the storm. Types of Maps ► Physical Map –shows land and water features. Uses colors to distinguish land from water. Types of Maps ► Political Map – shows the name and borders of countries. Also show the location of cities and other human-made features of places. Types of Maps ► Special Purpose Map – Shows specific kinds of information such as population density or a route taken in a war. Choropleth Map ►A dot distribution map (also known as dot density map) is as a map type that uses a dot symbol to show the presence of a feature. Dot maps rely on a visual scatter to show spatial pattern. Reading Maps ► Key/Legend map. ► Map – Explains the symbols on a Scale – shows how distance is represented in a map Reading Maps ► Compass Rose – shows us the cardinal directions of North, South, East, and West. Using Charts, Graphs, and Diagrams ► Charts Show facts in rows and columns Look at labels at the top of each column ► Graphs Bar graphs to compare data Line graphs to show changes over time Climate graph combines both (climograph) Pie graphs show the entire part and is divided into parts ► Diagrams Special drawings