* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Imperialism
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
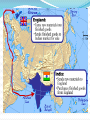
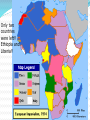
Imperialism Words to Know: Imperialism: Foreign policy when a stronger nation takes over a weaker nation or region and dominates its economic, political, or cultural life Colonialism : The policy of maintaining colonies as a source of raw materials and new markets. Practiced during old and new imperialism. Raw Materials: Various materials found in nature used in manufacturing such as wood, coal, and oil. Culture: The shared beliefs, customs, practices, and social behavior of a particular nation or people Words to Know: Nationalism: pride and devotion to one’s country Nationalist take pride in nation, culture, history and government Feel that their country is the best! When?? Old Imperialism 1500-1600s Europe starts expanding to Asia, Africa and the Americas Great Britain takes over N. America and Spain takes over S. America When?? New Imperialism 1800s 19th Century Industrial Revolution Create Empires Increase Nationalism How? What? Imperialism is a foreign Only Industrialized policy How a country deals with other countries Countries created empires by building colonies Countries Ships and Guns Technology Navy Army Who?? Ten Imperialist Powers Great Britain, Germany, France, Italy, Japan, Netherlands, Russia, Spain, Portugal, and the United States Only two countries were left!! Ethiopia and Liberia!! Motives of Imperialism/ Causes Economic •Motive is $!! •Raw Materials •Imports and Exports Political •World Power!! Competition •Protect Investments •Establish own Gov. Military •Strategic Locations! Strength and Security (gas stations) Cultural •Superiority •“Duty to Help” Religious •Missionaries •Moral Issues Imperialism: The Scramble for Africa Industrialism and Imperialism The Industrial Revolution created a desire for natural resources. 2. Many of these resources were not available in Europe. 3. Since much of the American colonies became independent, European powers looked to Africa and Asia for new colonies. 1. Imperialism: The Scramble for Africa Europeans ruled their colonies with total authority, and they were not afraid to use force. 2. Indigenous people were used as slaves in the extraction of natural resources. 3. Europeans used the concept of Social Darwinism to justify this. 4. Social Darwinism: The belief that people and societies evolve like nature. The most technologically advanced cultures are believed to be superior to others. Leads to racism. 1. Social Darwinism Herbert Spencer: The Founder of Social Darwinism Imperialism: The Scramble for Africa Paternalism Social Darwinism inspired the concept of Paternalism. 2. Paternalism stated that the societies of Asia and Africa could not run their own governments and need Europeans to take care of them. 3. Paternalism= Parents 1. Imperialism: The Scramble for Africa Assimilation- Along with Paternalism came the concept of Assimilation. This stated that Indigenous peoples would assimilate into European culture. Imperialism: The Scramble for Africa The Berlin Conference By the middle of the 1800’s, it seemed clear that European powers were going to war over colonies in Africa. 2. In order to avoid this, the leaders agreed to meet in Berlin to cut up “the African Cake.” 3. In 1884 and 1885 Europe divided up Africa. 1. Imperialism: The Scramble for Africa The African Cake Imperialism: The Scramble for Africa The Division of Africa by the Berlin Conference Imperialism: The Scramble for Africa The Europeans Extracted Wealth from Africa Imperialism: Ethnic Warfare and Poverty Imperialism: Ethnic Warfare and Poverty Apartheid in South Africa Mandela and F.W. de Klerk United Streaming Clip Mandela Imperialism: British Imperialism in India Starting in the 1600s the British began to dominate India. By the 1800’s, it ruled it through the British East India Company. Imperialism: British Imperialism in India Indian Servitude Imperialism: British Imperialism in India Even in the face of famine the British still pushed cash crop production. Imperialism: British Imperialism in India A Sepoy Soldier- Indians were used as soldiers by the British Gandhi United Streaming Mao Zedong “Political power grows out of the barrel of a gun” Gandhi “Victory attained by violence is a tantamount to a defeat, for it is momentary” Imperialism: Southeast Asia is Divided Map showing the Division of Southeast Asia Imperialism: China Resists Imperialism The Qing Dynasty Resists the British The Qing did not want Western influence in China. 2. However, Westerners (especially the British) wanted Chinese goods (i.e. tea). 3. The Chinese forced Westerners to trade through Guangzhou (Canton) in exchange for precious metals. 1. Imperialism: China Resists Imperialism The British solution was to introduce opium as a trade item. As the Chinese population became addicted to the drug demand skyrocketed. “By what right do they [British merchants]… use the poisonous drug to injure the Chinese people?... I have heard that the smoking of opium is very strictly forbidden by your country; that is because the harm caused by opium is clearly understood. Since it is not permitted to do harm to your country, then even less should you let is be passed on to the harm of the other countries.” Emperor Lin Zexu Imperialism: China Resists Imperialism The Opium War War broke out in 1839 between the Qing and the British. 2. It became known as the Opium War because the Qing wanted to end the trade of Opium. 3. Industrialized Great Britain won easily and gained full trade access to China. 1. Imperialism: China Resists Imperialism The Taiping Rebellion In the 1850s, China experienced the bloodiest civil war in human history. 2. Hong Xiuquan began a Christian religious sect known as the Taiping. 3. He led a revolt against the Qing. 4. The war would eventually cost 20 million lives. 1. Imperialism: China Resists Imperialism The Qing were forced to turn to the West to aid them in defeating the Taiping. They used Western weapons. This only gave Western countries more access to China. Sphere of Influence Open Door Policy Area in which foreign nation U.S. declared China to be controlled trade and investment open to merchants of all nations Imperialism: China Resists Imperialism The Society of the Righteous and Harmonious Fists- A group in China which sought to push foreigners and their influence out of China. Westerners called them Boxers. Imperialism: China Resist Imperialism The Boxer Rebellion In 1900, the Boxers surrounded the foreign section of Beijing and laid siege to it. 2. Western armies responded by invading China and putting down the Boxers. 3. The war became known as the Boxer Rebellion. 1. Imperialism: Japan Although Japan had a “Closed Country Policy,” the United States Navy forced it to open up trade in 1853. U.S. Commodore Matthew Perry Imperialism: Japan The Meiji Restoration Soon after, Emperor Mutsuhito wrestled control away from the Tokugawa Shogunate. 2. He started the Meiji Period. 3. The Meiji sought to modernize Japan on the Western model in order to resist the West. 1. Imperialism: Japan Meiji Modernization Imperialism: Japan Sino-Japanese and Russo Japanese Wars Compare and Contrast China and Japan China Japan Forms of Imperialism Form Definition Example Colony Country or territory governed internally by a foreign power 13 original US colonies Protectorate Country of territory with Puerto Rico its own internal government but under the control of an outside power Sphere of Influence Area in which an outside power claims exclusive investment or trading privileges China Economic Imperialism Independent but lessdeveloped country controlled by private business interest Dole Fruit Company controlled Hawaii Imperial Management Methods Indirect Control Direct Control •Local Government officials •Limited Self-Rule •Goal was to develop future leaders •Government institutions are based on European styles but many have local rule •Foreign officials brought in to rule •No self-rule •Goal was assimilation •Government institutions are based only on European styles Examples: •British colonies such as Nigeria, India, Burma Examples: •French Colonies such as Somaliland or Vietnam •German colonies •Portuguese colonies •US Colonies in the Pacific