* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
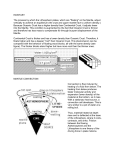
Earth Structure Recap. Use arrows to locate the labels on the left hand side. 400°c 5270 km 2900 km 6370 km depth 5000°c Inner Core Mantle Asthenosphere 3000°c Outer Core Lithosphere Say which is the odd one out and explain why. Inner Core Crust Outer Core Mantle Core Convection Earthquake Convection Volcano Why are the core and mantle of the Earth so hot and how does this heat affect life on the surface of the planet? Key words Radioactive Decay, Convection Currents, Plate tectonics, Earthquakes, Volcanoes, magnetism. …………………….…………………….…………………….………………….…………………….…………………………….. …………………….…………………….…………………….………………….…………………….…………………………….. …………………….…………………….…………………….………………….…………………….…………………………….. …………………….…………………….…………………….………………….…………………….…………………………….. …………………….…………………….…………………….………………….…………………….…………………………….. …………………….…………………….…………………….………………….…………………….…………………………….. …………………….…………………….…………………….………………….…………………….…………………………….. …………………….…………………….…………………….………………….…………………….…………………………….. …………………….…………………….…………………….………………….…………………….…………………………….. …………………….…………………….…………………….………………….…………………….…………………………….. …………………….…………………….…………………….………………….…………………….…………………………….. …………………….…………………….…………………….………………….…………………….…………………………….. Extra info! - Find out who Lord Kelvin was and what he calculated. Contrasting Crustal Components A sample of Granite A sample of Basalt • • • 2.9 grams per cm cubed Cools quickly close to the surface or as lava erupted from a volcano. Contains less than 20% Quartz and large amounts of Magnesium. • • • 2.6 grams per cm cubed Cools under ground slowly from magma allowing large cristals to grow. Contains mostly Silica with at least 20% Quartz. In your exam you may be asked to CONTRAST geographic features or processes. This means say how they are DIFFERENT. Exam question (4 marks) Contrast the two types of the Earths crust. There are two types of Crust, Oceanic and Continental. Continental crust is light with a density 2.6 times that of water, it also has a lot of Silicon. Oceanic crust is called basalt which is a dark rock which has cooled quickly so has small cristals. It has a high density of 2.9 as it has dense minerals in it. How many marks would you give the answer above and why? What words can you use to contrast the two types of crust? However, on the other hand, alternatively, whereas Denser, Darker, more slowly, larger cristals Extension Exam question (8 marks) Describe two different types of the earths crust and explain what happens when they collide and why.