* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Phylum Porifera: Sponges
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Stem-cell therapy wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
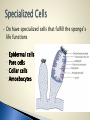
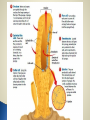
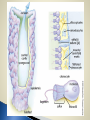
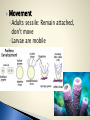
Biology 11 Name means “pore bearers”- body has many pores in it Sessile Multicellular Mostly marine (only 100/9000 are freshwater) Asymmetrical body shape Made of 2 cells layers ◦ Ectoderm ◦ Endoderm No specialized tissue or organ systems ◦ Individual cells sense and react to environmental changes Do have specialized cells that fulfill the sponge’s life functions ◦ Epidermal cells ◦ Pore cells ◦ Collar cells ◦ Amoebocytes Epidermal cells form outer covering Water is drawn in through pore cells into a central cavity The collar cells have flagella that beat to create a current to make sure water is being drawn in through pore cells Water flows out of sponges through a larger opening called the osculum Make spicules ◦ Needle-like structures that provide structural support ◦ Made of silica or calcium carbonate ◦ Some made of spongin protein (softer skeleton) Carry nutrients to other cells Aid in reproduction Contain a flagellum to move water in Brings oxygen and food particles into body of sponge Water acts as the circulatory, respiratory, reproductive, and excretory systems Brings in food, oxygen, carries away waste, gametes, larvae Oxygen is brought in and carbon dioxide and other metabolic wastes are given off Feeding and Digestion ◦ No mouth or digestive tract ◦ Are filter feeders- sift food particles from the water Driven by water flow Filtered by collar cells Excretion ◦ Driven by water flow Respiration ◦ Oxygen diffused from surrounding water into cells ◦ Carbon dioxide diffused from cells to surrounding water Movement ◦ Adults sessile: Remain attached, don’t move ◦ Larvae are mobile Sexual Most are hermaphrodites (produce both egg and sperm) Sperm released out of osculum and swim to another sponge (with the help of currents) ◦ Enter another sponge’s pore cell ◦ Picked up by collar cells ◦ Carried to an egg by amoebocytes ◦ Fertilization occurs ◦ Zygote develops into a flagellated larvae which is mobile (can be dispersed) Increase change of fertilization They do not fertilize their own eggs with their own sperm Can also reproduce asexually by: ◦ Fragmentation: part of sponge breaks off ◦ Budding: mitotic growth and break off ◦ Gemmules: collection of cells that are enclosed by hard outer covering contain spicules Form when conditions are unfavourable Provides habitat for many other animals ◦ Like snails, shrimp, sea stars, bacteria… Is a food source for other animals Provides a symbiotic relationships with bacteria (bacteria provide food and oxygen to sponge and remove wastes) Used as bath sponges Produce chemicals (to discourage other animals from eating them) that are being used in research for cancer, viruses, and antibiotics